Scams in Australia February 2026: types, latest cybercrime trends and how to protect yourself
Stay scam savvy with our in-depth and regularly updated guide

Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
- AI-powered attacks are on the rise in 2025
- Scams are becoming more personalised and harder to spot
- Hacks of major Australian companies ongoing
- Networked home appliances can be a security risk
- Windows 10 users will stop getting security updates after 14 October, 2025
How vulnerable do you feel using your smartphone and computer? If it’s not the constant blitz of malware and adware, it’s a steady stream of newly discovered vulnerabilities that could result in all kinds of information leaking out onto the internet. In this article, we’ll keep you up to date with the latest digital threats, and show you how to protect yourself and your identity online.
Things are a lot more complicated in 2025 than ever before. Cybercriminals are now harnessing the power of AI to make ever more effective attacks. This has given rise to the use of AI in cybercrimes including crafting custom phishing emails, generating malware, and automating cyberattacks.
On the increase are unsolicited ‘advance fee fraud’ (also commonly known as ‘Nigerian prince’ or ‘419’ scams) emails and SMS messages, which are sent by the thousands every day. Although the wording varies, the usual premise is that a wealthy individual like a prince or industry tycoon has died, and the sender needs your help to recover their lost millions in exchange for some personal details and a small ‘processing fee’.
Anyone who’s fooled into responding never sees their money again. Scammers usually ply victims with excuses as to why they must send more funds for supposed administrative and legal fees.
Phishing emails follow a similar pattern whereby a scammer impersonates a trusted person like a colleague, then encourages the recipient of a message to open an attachment or URL that leads to a phishing domain and/or malware.
Traditionally, a key tell that such emails aren’t legitimate has been where the sender uses poor spelling and grammar, even though they’re supposedly writing in their native language.
Unfortunately, fraudsters have been quick to spot that generative AI can iron out typos, as well as other linguistic quirks that might reveal that such messages aren’t genuine. This has ushered in a new golden age, dubbed ‘AI phishing’.
Being alert and aware is still the most effective way to keep these at bay, as well as using your device’s in-built security protections.
Telstra has given the following advice on stopping scams before it's too late:
- Pause before responding: don't message back, even if you're typing 'no'
- Be sceptical of easy offers: a job or deal that seems too good to be true often is
- Verify through official channels: check for information about the contents of a message on the company's official website (as the scammer may be impersonating)
- Be suspicious: even when the caller knows your name or specific credentials, they may be attempting to extract sensitive information or cash
- Protect your ID: do not give up personal information to unknown people
- Be wary of emotional tricks: if a message seems urgent, be aware that the scammer may be trying to force you to act before thinking
- Use security tools: antivirus tools and device security software can help stop scams at the start
- Embrace your 'scammer sixth sense': trust your gut and know something can be too good to be true
New and trending scams and breaches – 2025 (updated 19/12/2025)
13,000 individuals’ records hacked in Sydney University attack
Personal data from 7,945 staff, and around 5,000 former students was stolen from a database run by Sydney University, in a recent cyberattack.
According to information provided by Sydney University, the attack targeted a database holding personal information that was valid as of September 2018. This information includes the name, date of birth, phone number and home address of staff who were employed at the time, as well as some basic job information (e.g. job title and employment dates).
Sydney University has begun notifying those affected, and is implementing steps to minimise the damage. It has also commenced a formal investigation into the cyberattack. The University recommends that those affected should change their passwords and implement multi-factor authentication where possible.
An FAQ page has been created here, and a central information page here will be kept updated.
The cyberattack gained access to the following data:
* personal information of around 10,000 current staff and affiliates, that were employed or affiliated as at 4 September 2018
* personal information of around 12,500 former staff and affiliates, that were employed or affiliated as at 4 September 2018
* a series of historical data sets predominantly from 2010-2019 containing personal information of around 5000 alumni and students, as well as six supporters.
Sydney University says it is directly contacting current and former staff, students and alumni affected by this incident.
AI-powered scams rise steeply
The use of AI by cybercriminals has soared during 2025, with millions of scam-related domains detected during the March to October 2025 period.
According to a report released by Nord VPN today, AI has become a dangerous weapon in the hands of criminals.
“Scammers are evolving at an unprecedented pace, using AI not just to automate attacks but to make them deeply convincing,” says Marijus Briedis, chief technology officer (CTO) at NordVPN.
Among the biggest risks are AI-generated phone calls that impersonate financial institutions. Even more alarming is an increase in calls that impersonate a voice someone receiving a call might know personally.
AI-driven scams are growing in sophistication, with emails and SMS messages now "highly believable", according to NordVPN.
“AI is a double-edged sword: while it powers incredible innovations, it also equips scammers with tools to mimic legitimate communication flawlessly,” explains Briedis. “This fusion of AI and social engineering creates a challenging landscape where technology alone isn’t enough; users must stay alert and question what they see and hear.”
Also of note, investment scams have increased by almost 25% year by year. The number aren't small – during 2024 the FTC in the US reported that USD$5.7 billion was taken by fraudsters using investment scams alone.
To avoid being caught out yourself, it's imperative that any unsolicited offers or opportunities be carefully scrutinised. If any unusually high investment returns are being offered, take extreme caution by looking at the URL they present and avoiding anything suspicious. Also be alert to unusual templates and formatting in emails and text messages.
“Enabling identity monitoring and alerts can help detect data breaches early, while multi-factor authentication adds an essential layer of security. Consumers should also consider cyber insurance and educate themselves about emerging threats like deepfake voices, impersonation, and fake shops,” says Briedis.
Western Sydney University hacked again, some student's personal info stolen
Type: Personal data stolen
Currency: October 23rd 2025 - ongoing
In the latest of a series of attacks since May 2024, Western Sydney University has reported a new cyber incident.
According to information provided on its dedicated Cyber Incident site, the university has said "attempts to gain unauthorised access to our systems have continued, including via external parties that supply IT services to the University. In recent weeks, it has become clear that these incidents are intended to harm our community."
The University and NSW police are investigating the attacks. Western Sydney University has not stated how many students have been affected, though it has posted that personal information that may have been impacted includes:
- Contact information (address, email address, phone number)
- Name, date of birth, student or staff ID
- Country of birth, nationality, citizenship and/or gender or identity information
- Ethnicity
- Employment and payroll details
- Bank account details
- Tax file number
- Driver licence details
- Passport details
- Visa information
- Complaint/case information
- Health and disability information
- Legal information.
The University has contacted those it believes have been impacted.
What you should do: Be alert to fraudulent emails and immediately change your relevant passwords, and use a strong password. New information regarding this and other attacks will be posted on the University's Cyber Incident site.
Qantas hack sees over 5 million accounts stolen
Type: Personal data stolen
Currency: October 11th 2025 - ongoing
On Saturday October 11th a cybercrime group known as Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters has dumped the customer records of more than 5 million customers on to the dark web.
The leak follows an attack on Salesforce in July, after which the hackers demanded a ransom to prevent the release of the information to be paid by Saturday Octover 11th. It appears the ransom was not paid, and the group has begun posting customer data online.
Qantas have moved quickly to assure its customers that no financial data has been leaked. On its site the company stated: "Passwords, PINs, and login details were not accessed or compromised," the statement said.
"Qantas confirms that no identity documents, credit card numbers, or personal financial details were accessed or compromised as a result of the incident."
However, the stolen information has the potential to be used for phishing and social engineering hacks.
What you should do: Take extra care to verify any emails or messages that appear to come from Qantas, or are related to Qantas in any way.
Small businesses vulnerable to ransomware
Type: QLD pharmacy business data potentially accessed
Currency: September 2025 – ongoing
The Friendlies Society Dispensary in Toowoomba has potentially had data kept on its IT systems breached via a ransomware attack. The ABC reports that an investigation is underway to determine the extent of the attack. A combined effort by the National Office of Cyber Security, the Australian Cyber Security Centre, Services Australia, the National Disability Insurance Agency, Queensland Health and the Department of Home Affairs is looking into possible data theft, and its impact on the business and its customers.
What you should do: Experts advise that any small business that faces a ransomware threat should not pay the hacker's demands, as there is no guarantee that paying up will remove any stolen data from the dark web, and elsewhere.
iiNet
Type: Customer personal data stolen
Currency: 19 August 2025 – ongoing
Popular Australian ISP iiNet had its customer database hacked in August 2025, leading to up to 280,000 email addresses and phone numbers being taken. iiNet announced the hack in a statement on its site on 19 August, saying: “The iiNet ordering system is used to create and track orders for iiNet services, such as NBN connections. The system contains limited personal information. Importantly, it does not contain copies or details of customer identity document details (such as passport or driver’s licences), credit card or banking information.”
Furthermore, it appears that some customers have had more personal details stolen, with iiNet saying: “In addition, around 10,000 iiNet usernames, street addresses and phone numbers and around 1,700 modem set-up passwords, appear to have been accessed.”
What you should do: iiNet has issued the following advisory: “iiNet urges our customers to remain vigilant, especially to any suspicious communications received via email, text or phone call. If in doubt, contact iiNet directly or seek independent advice from trusted sources, including the Australian Cyber Security Centre at cyber.gov.au. We have set up a dedicated hotline at 1300 861 036 so customers can reach us if they have any concerns.”
Dreame robot vacuum app
Type: Smartphone app (iOS and Android)
Currency: Ongoing
Owners of Chinese robovac company Dreame could be at risk, with hackers able to extract password information when you use the Realme app. Users of the Dreame X50 Ultra vacuum could also be at risk of the unit’s camera being accessed remotely if sharing permissions were enabled. The vulnerability has been known for some time, but it only affects people that use public Wi-Fi to access the app.
In these circumstances hackers can extract login details, personal data as well as locate the house where the robovac is installed.
What you should do: Owners of Dreame robovacs should only use the associated app in a secure Wi-Fi environment, and never via public Wi-Fi, such as hotels or airports. Ensure you are always running the latest version and disable sharing permissions.
Victoria’s Loyola College
Type: Student personal information, passport info and financial records stolen
Currency: 1 September 2025 – ongoing
Melbourne’s Loyola College has had its IT systems infiltrated by hacker group Interlock, which says it has obtained more than 430,000 files, including the financial and tax records of employees past and present. The college has since upgraded its security, which includes changing all passwords for students and staff.
What you should do: Loyola College is communicating directly with current and former staff and students with updates and protective measures to take.
Latest Australian cybersecurity news
Apple’s new iPhones hardened against spyware and surveillance
Latest A19 chips feature hardware-level protection
With the recent launch of its new A19-powered iPhone 17 range, Apple claims to now offer much improved protection against spyware. The entire iPhone 17 range now features what Apple calls Enhanced Memory Tagging Extension (EMTE), which works to provide real-time defence against attacks.
Another new security feature that covers all iPhones pre-dating the iPhone 17 range has been launched, too, Apple announced. The new Memory Integrity Enforcement (MIE) feature increases spyware protection for those devices – provided they are upgraded to the latest iOS 26.
Windows 10 EOL almost upon us
It’s time to make the move to Windows 11, or an alternative secure OS
On October 14th, Microsoft will cease support for the popular Windows 10 OS. That means your PC will no longer be updated, and that leaves it vulnerable as new threats emerge after that date.
Upgrading to Windows 11 is the logical step for any Windows user, while Linux also offers a more secure alternative if you can live without Windows-specific apps. This guide covers the relatively simple process of switching to Windows 11.
Microsoft is also offering an extended Security Updates (ESU) program for the first time. It won’t be free though.
Read more: Want to stick with Windows 10 after October 2025? Here are your options.
VicRoads announces major security overhaul
Passwords – out, passkeys – in. Switch over expected by the end of the year
All 5 million VicRoads customers are being transitioned away from traditional password logins for their accounts, in favour of more secure passkey protection.
On behalf of VicRoads, Igor Igor Gjorgjioski, its head of digital channels and platform enablement said: “There have been many account breaches in Australia in past years, and passkeys are actually helping to improve security posture and protect customer accounts by being an efficient [attack] resistance and a form of MFA by design.”
Passkeys use a device’s built-in security instead of a simple password, which typically include smartphone biometric methods such as Touch ID or Face ID to authenticate a login.
You can find out more on VicRoads’ information page here if you are a customer.
Jargon buster
What is Smishing?
Similar to Phishing, Smishing is an attempt by hackers to obtain your personal information via a text message (SMS). Unlike Phishing, these attacks are exclusive to SMS. Often these appear to be from reputable companies, and lure the user into sharing their personal information, downloading malware or clicking on malicious links.
How to protect yourself: No company or organisation should ever ask you to provide any personal or account information directly via SMS. If you receive anything suspicious, ignore it, and report it as spam or a security attack via your devices’ SMS reporting options, and if in doubt contact the company or organisation purporting to be the sender to verify its authenticity.
Common scams in Australia
Below are several examples of common scams that can happen in Australia. These scams target Aussies over email, the phone, SMS, social media and through legitimate websites like Amazon and eBay, so when you receive a message or see a deal that’s too good to be true, remember to just think about it for a moment.
The ACCC recommends a three-step approach to thwarting scams:
- Stop: Don’t rush into a deal as scammers will typically create a sense of urgency to entice you into a mistake
- Think: Scammers typically impersonate businesses or government bodies that you know. Consider if what you’re being told makes sense depending on the sender, and before committing to anything, check with the business or government department directly
- Protect: If it feels wrong, act quickly to stay safe. Contact your bank immediately if you’ve shared any financial information or transferred money. Get in touch with Scamwatch to report the scam when you get a moment
Online romance scams
“Pig butchering” is a romance investment scam where the scammer forms a relationship with the victim, often making a connection through social media or dating apps, and hints at a lavish lifestyle earned through cryptocurrency. As the scammer earns the victim’s trust, they will direct the victim to put money into what looks like a legitimate investment site or app. These clones are convincing enough that people invest high amounts of money, but soon find out they are unable to withdraw their gains, with the scammer cashing out once the victim refuses to add any more funds into the scheme.
Scams like this have contributed up to AU$3,800 lost every hour in 2023 according to the Australian Federal Police, and it’s an ongoing issue in 2024.
Product and service scams

A common type of scam takes place when a scammer attempts to impersonate a legitimate website, or listings on a legitimate website, in an effort to syphon money from unsuspecting users without providing the service they think they’re paying for.
By Scamwatch’s definition, this is known as a product and service scam, and it can take place anywhere on the internet – be it a bargain deal on a website like eBay or Amazon, a dodgy listing on Airbnb or Booking.com, or a faked version of a website like Kmart. These scams prey on customers that don’t have great awareness of inauthentic behaviour on the internet, so it pays to do your research to uncover if a listing is from a reputable seller.
Phishing and impersonation scams
Phishing scams are quite common. Bad actors will send people texts or emails, or attempt to call them, to either harvest personal information from them (such as login information or addresses) or to take money from them directly. This is achieved by leading the user on and getting them to give this sensitive information willingly to the scammer, be it through a website, by texting or emailing it back to them. With this, a user’s personal information or bank account may become compromised.
These scams often overlap with impersonation scams, where a scammer will pose as an established business or government authority to seem more legitimate.
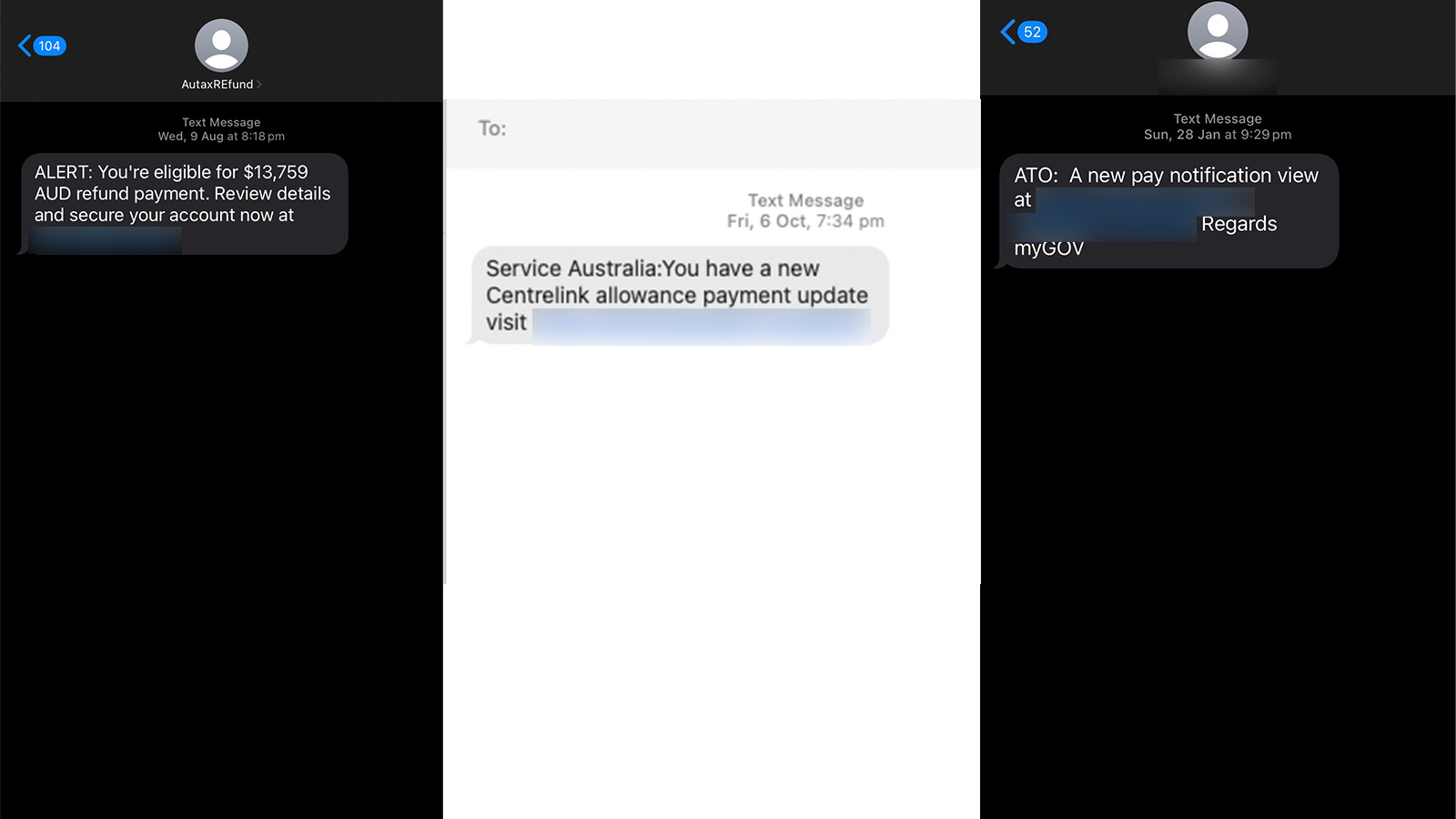
Fake job scams
A type of scam that is on the rise in 2023 and 2024 is the fake job scam, where a scammer will pose as an employer of a business eager to hire you, but will require you to send them cash first. Any job that requires you to pay the business upfront before you start should be examined and considered carefully, as you’ll often be offered a position that’s too good to be true. It’s also common for scammers to pose as a recruitment agency to conduct this kind of scam.
Threats and extortion scams
Scammers may attempt to extort money out of you by threatening with a virus, a fee or an unpaid bill. While scammers that are threatening and extorting a person may fall under the impersonation scams category, there’s also space to talk about scammers leveraging world events in an attempt to get money out of your account.
A good example is the CrowdStrike outage, in which millions of computers internationally needed to be manually rebooted, as they were stuck in a constant bluescreen boot loop. Scamwatch reported in July 2024 that scammers were using the outage to request personal information or cash to ensure that their devices or businesses wouldn’t fall victim to the issue.
‘Hi Mum’ impersonation scams
Bad actors may attempt to get in touch with you by impersonating a real person that you know well, such as your son or daughter, and ask for cash directly.
In 2023, these quickly became known as ‘Hi Mum’ scams, where a scammer would attempt to leverage goodwill with somebody they were pretending to be related to in an attempt to get them to send cash. Remember: if somebody you know is asking for cash or sensitive information, get in touch with them directly outside of the communications you’re having with a supposed scammer. It’s also important to not act too hastily, lest you make a mistake.
These scams may not necessarily have any ‘Hi Mum’ identifiers and could, instead, pose you with a scenario – for example, the texter ID could read ‘Dad’ and the message could say that they left their card at home and want money for a transaction. If you don’t know them, don’t follow through with it. If you do know them, but the message isn’t from their usual number, call the number you’re used to and find out directly.
Unpaid tolls
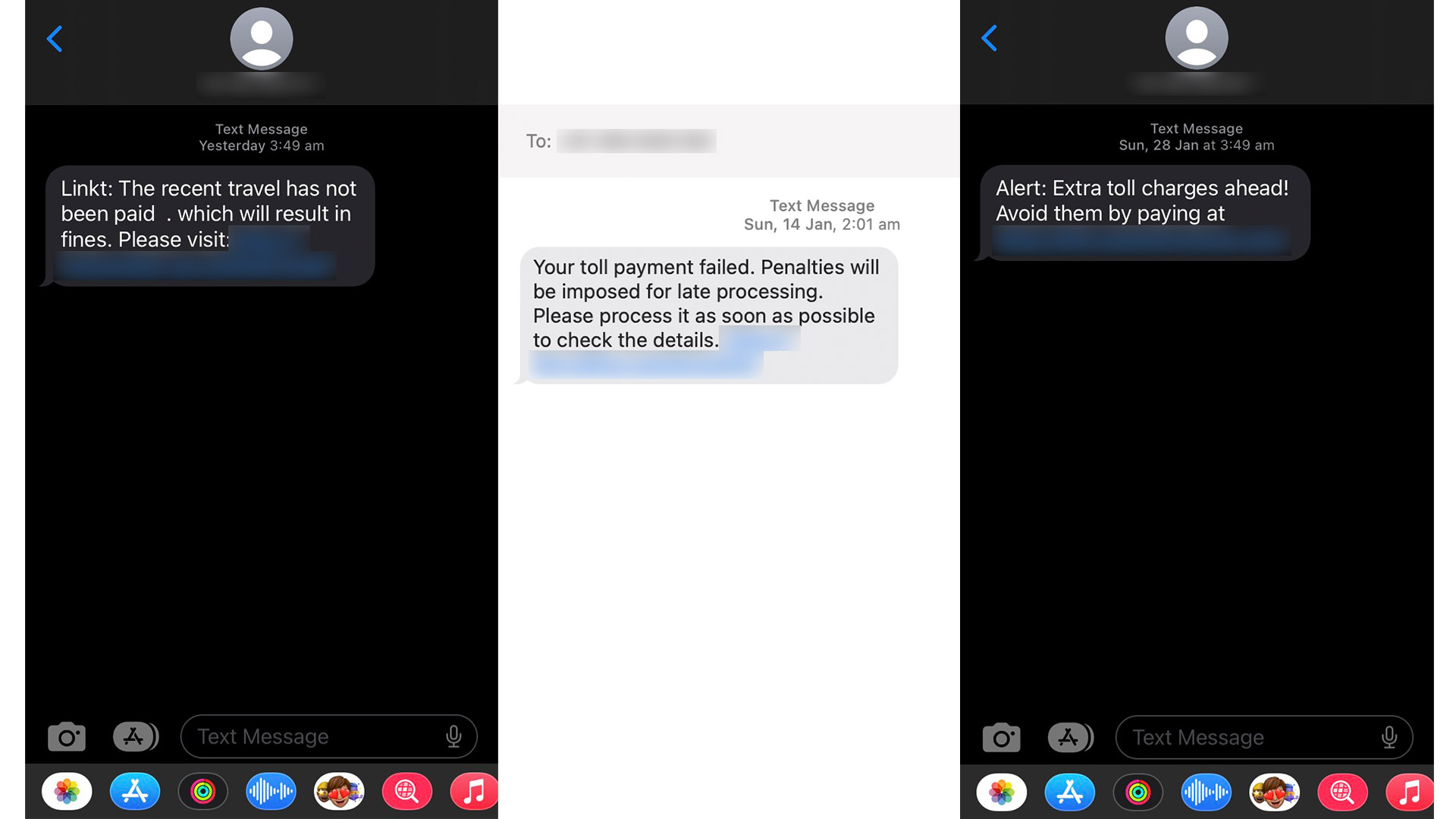
A common scam that peaks during certain times of the year has to do with unpaid tolls. In this instance, an email or text message is sent claiming that you haven’t paid your toll fees, and urging you to pay it ASAP via a suspicious link. It’s easy to spot if you don’t drive near any toll roads, but if you’re a frequent driver, the scammer is hoping you’ll panic and click through to pay your fake overdue fees before you realise what’s actually happening.
False delivery texts
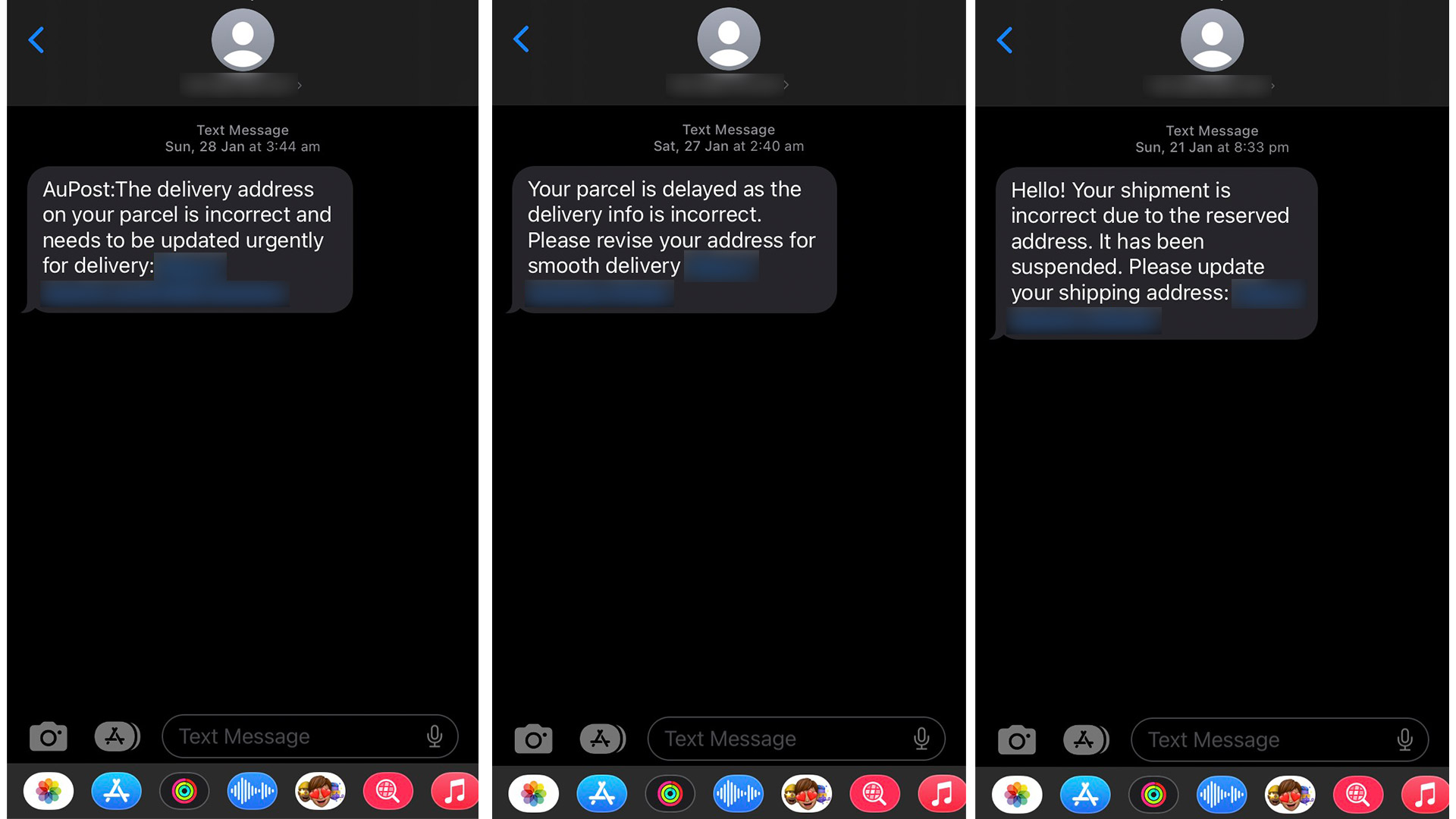
Have you received multiple unexpected SMS messages regarding undeliverable parcels? We certainly did – several members of our team provided snapshots of frequent text messages from random mobile numbers claiming that their delivery address needed to be updated. Often, these would be received around the same time, either in the morning, hoping to catch people who have just woken up, or in the evening, multiple times a week, pretending to be from companies like Australia Post. They would include suspicious links to ‘solve’ the delivery issues, which will lead the recipient to dodgy websites that can steal your information – never click on those links.
Subscription renewal/new sign up scams

There’s a subscription service for just about anything, and scammers have been known to impersonate brands, as well as create fake ones, in order to try and get your money or extract valuable personal information such as passwords. A subscription renewal or new sign up scam typically involves you being contacted unexpectedly via email, text or phone call by a scammer impersonating a brand. For example, the scammer may claim to be a representative from Amazon, and they may create a sense of urgency to renew your membership or subscription through a malicious link.
Facebook Marketplace & PayID scams
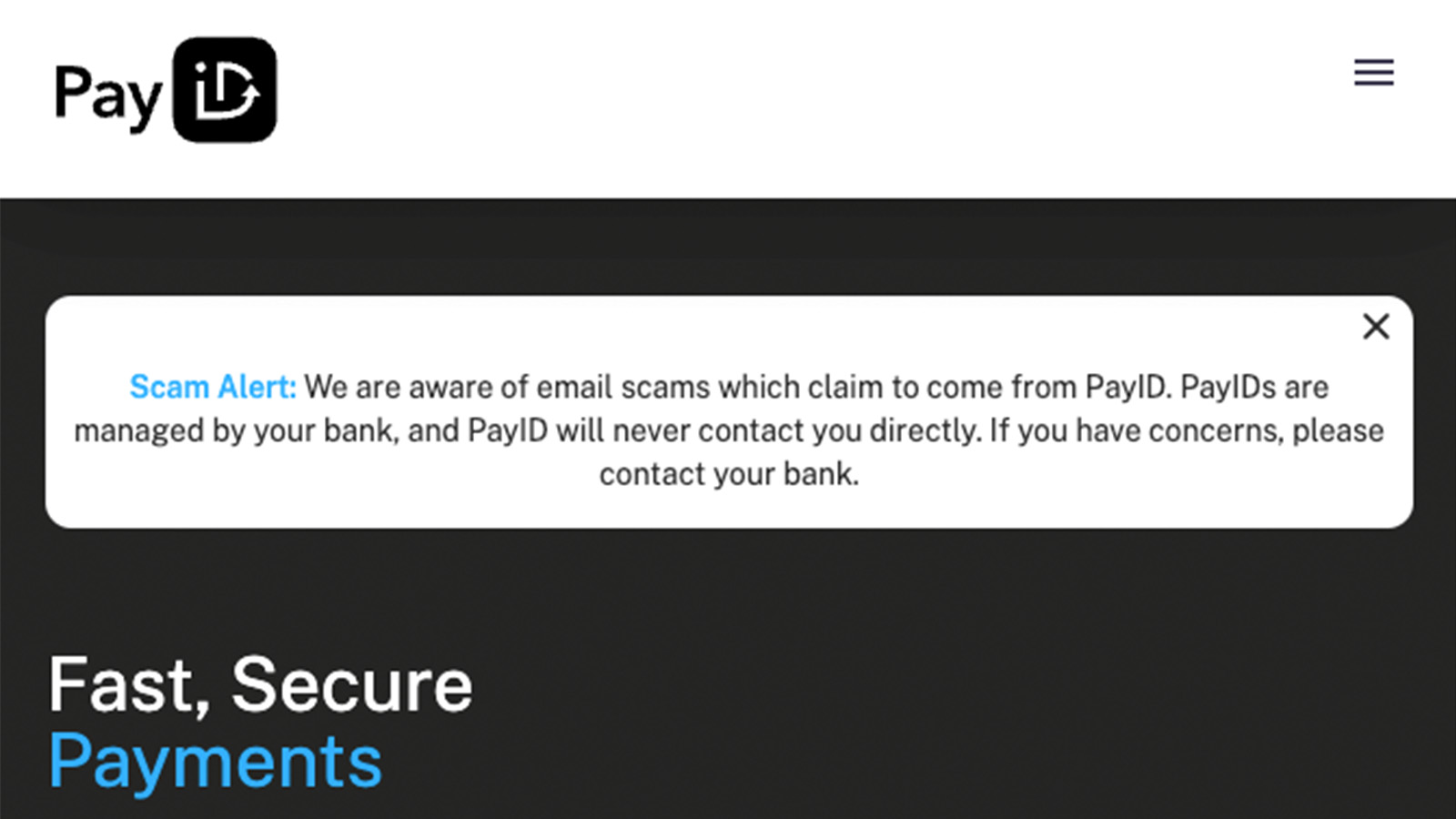
Scams on Facebook Marketplace and similar websites can target both buyers and sellers, and listings themselves can be for products that don’t exist. One particular scam on Facebook Marketplace which targets sellers involves a buyer requesting to make a payment via PayID, which means the seller will have to share their phone number or email. The seller will then receive a fake PayID email or text message, claiming that their PayID account requires a minimum amount and the scammer will offer to pay the extra so long as they get a refund right away. However, the unsuspecting seller is then left out of pocket with no successful sale if they follow through with it.
Fake celebrity endorsements
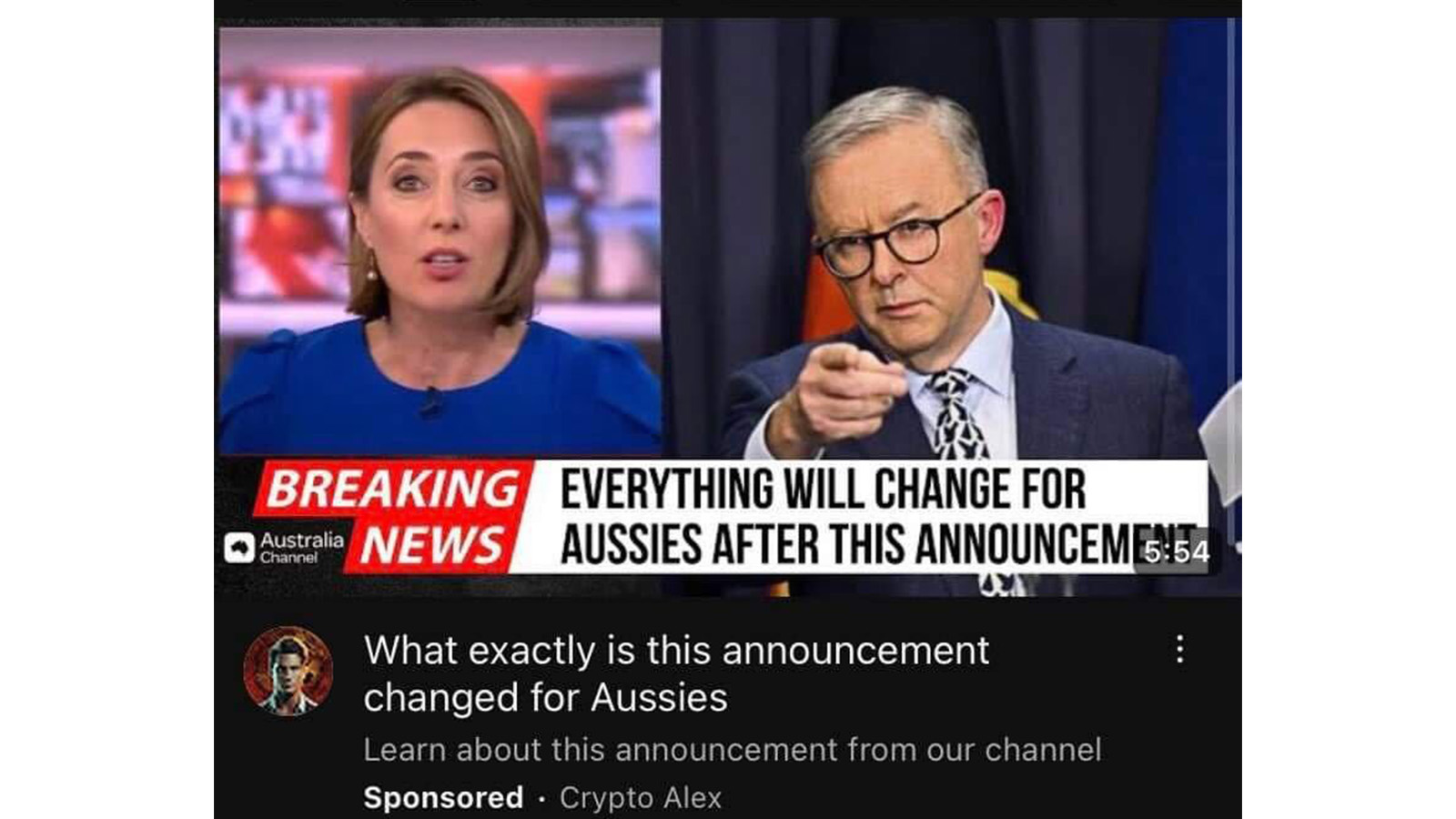
These scams tend to be found as advertisements on websites including Facebook and YouTube (but can really pop up anywhere, including on major news and entertainment websites) where the scammer has paid for a sponsored ad placement. They feature a well-known Australian individual such as a celebrity or politician, who’s being impersonated through video manipulation or photo editing, often with an outrageous claim alongside the image. The ads will often use a salacious ‘clickbait’ style heading, such as claiming to expose a shocking scandal, or tips for getting rich with cryptocurrency.
Current Prime Minister Anthony Albanese, TV personalities David Koch and Richard Wilkinson, entrepreneur Dick Smith, and many other prominent Australian figures have been impersonated online to try and con users into clicking onto sites that could have malware, or attempt to trick you into providing personal information or invest in too-good-to-be-true cryptocurrency schemes.
Unofficial ticket resellers
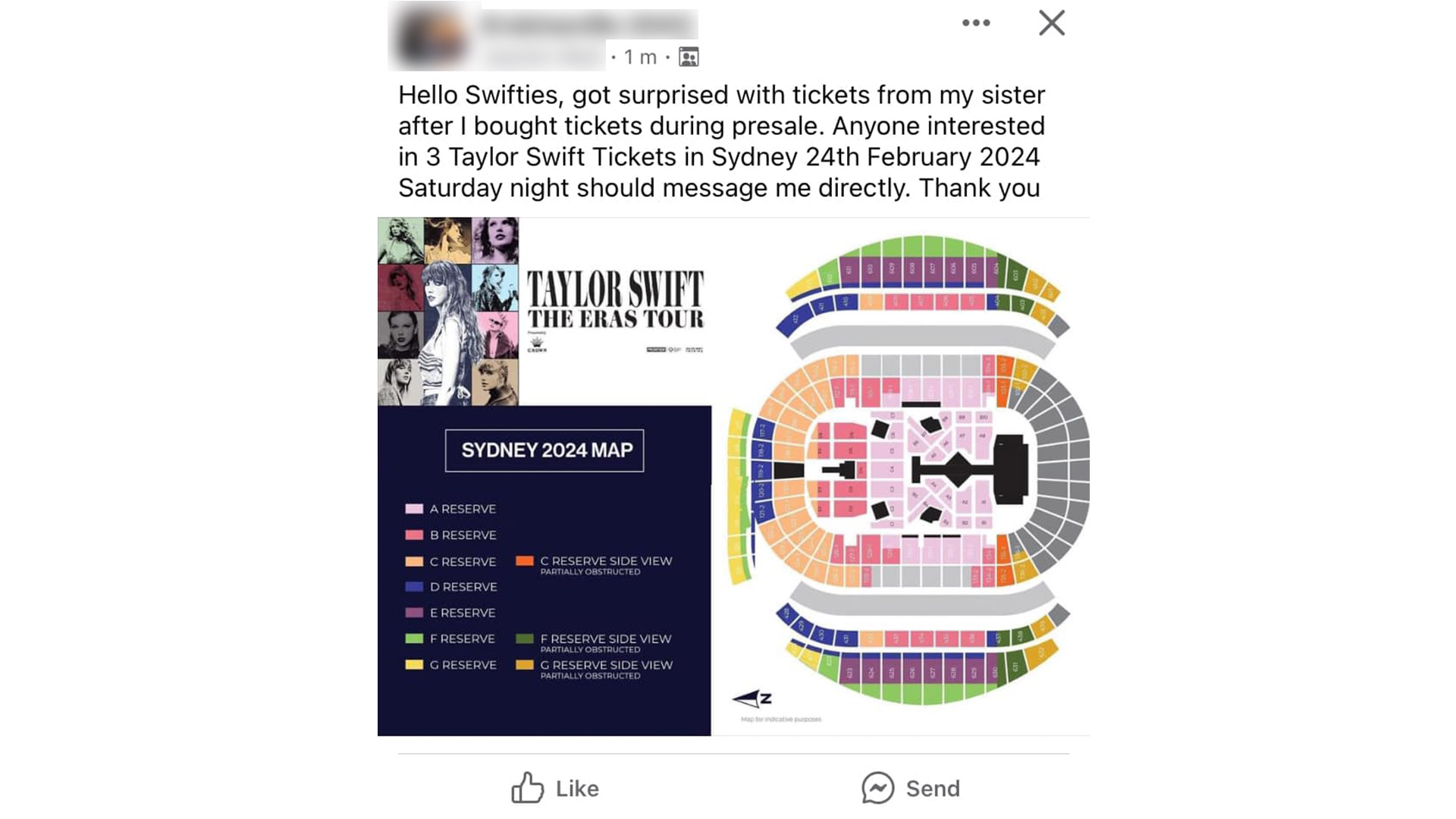
Unofficial or fraudulent ticket resellers is another form of a buying or selling scam. With big artists often touring Australia, many fans are desperately trying to find tickets to massive sold-out concerts. You should be very careful about buying tickets from unofficial resellers however, as this is a prime opportunity for scammers to take advantage of keen concert goers by selling fake tickets through places including Facebook Marketplace, eBay and Gumtree. We highly recommend you go through official resellers, such as Ticketek Marketplace and Tixel, for each concert, otherwise you might suffer from more than just FOMO.
Fake products
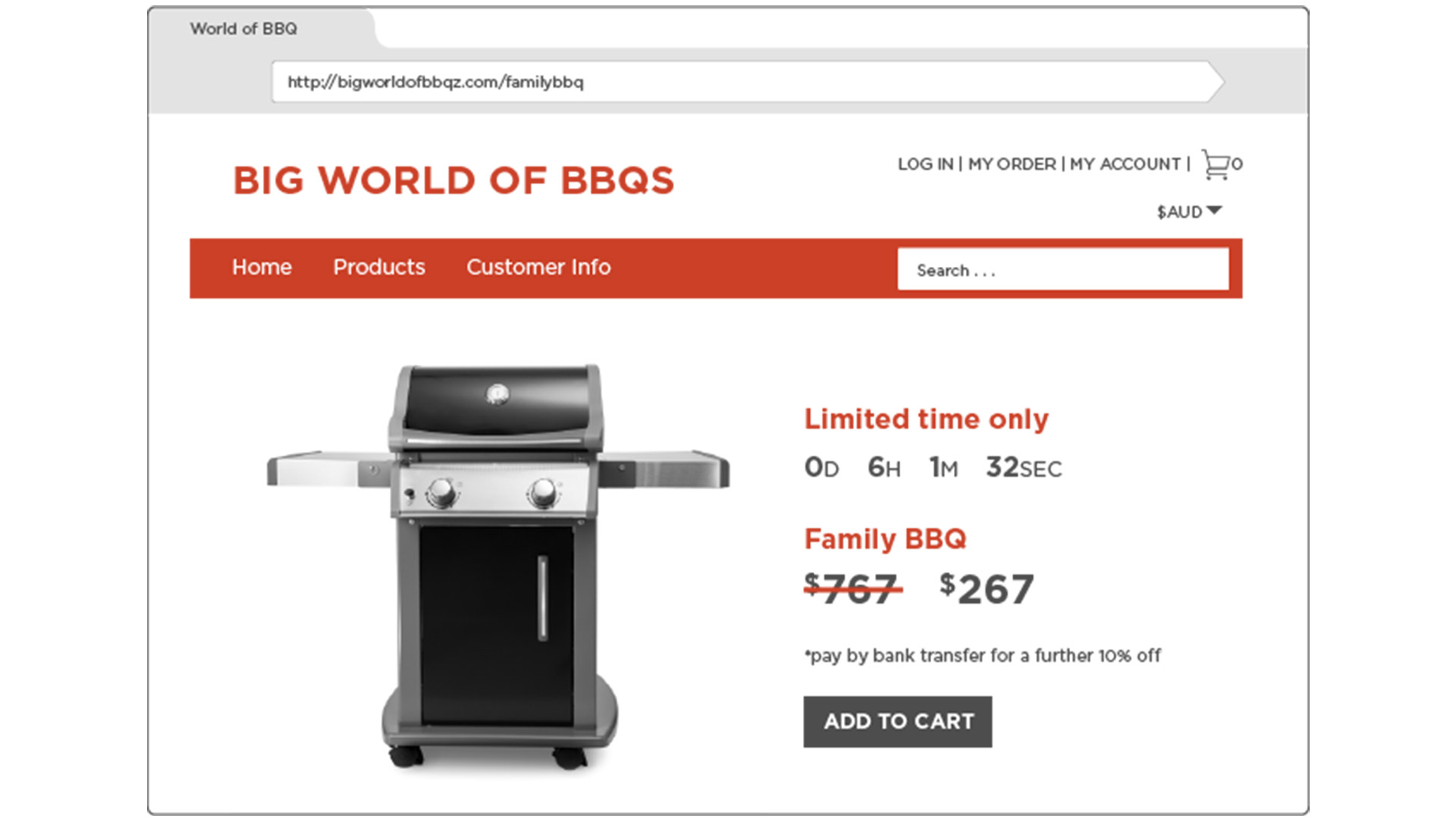
Since the early days of online shopping, consumers have been reporting scams involving false advertising. This is an ongoing issue to this day, with scammers often copying the details from a legitimate product listing and posting it on a fake website or under a fake profile on a genuine one. The scammer poses as a real online seller by promising products they don’t actually have, and instead sending unaware buyers junk knock-offs or nothing at all. Places such as Temu and Wish have been known to have product listings like this, but it’s an issue found far and wide across the web.
Scams in Australia: key information
What is a scam?
A scam is a scheme that attempts to steal either money or personal information from an unsuspecting party (either an individual or a business) through lies, manipulation and false pretences. Scammers are able to reach more people now than ever due to evolving communication technologies – you can be scammed in person, on the phone, through text messages or emails, across social media or simply by visiting a fake website. Each and every year there are new scams popping up, though these typically fall under one of seven major categories.

What are the different types of scams?
According to the ACCC’s Scamwatch, there are seven main types of scams:
Romance scams
These scams involve convincing someone into, or promising some kind of relationship, including both romantic and platonic, so the scammer can take advantage of the unsuspecting party’s finances.
Investment scams
In this case, the scammer will try to get you to invest in some scheme – it could involve something like cryptocurrency, NFTs, or some other get-rich-quick opportunity that involves an initial monetary investment from you to get started. Investment scams typically involve the loss of large sums of money, and can be devastating to both individuals and businesses.
Product and service scams
Product scams have been rife since the early days of the internet – we’ve likely all heard the horror story of someone buying a product only for it to be something completely different on arriva, or never show up at all. These scams still exist, and can even take the form of a service rather than a physical object. Basically, with this type of scam, you don’t get what you pay for, and can even put your sensitive information such as payment and contact details at risk.
Threat and extortion scams
Some scammers will threaten to cause some form of harm to you or someone you know if you don’t go along with a request. These types of scams might suggest they have compromising photos, or claim to hijack your PC among other scary situations in order to take advantage of your fear and urgency.
Jobs and employment scams
It can already be a challenge to find a job, and scammers have found ways to use this to their advantage. A job or employment scam might involve some monetary contribution to hold a promised position offered to someone, or it could involve false job advertisements where your information is stolen on application.
Unexpected money
If it’s too good to be true, it likely is. While we’d all like to win the lotto, you need to play it safe if you get a sudden message saying you’ve won a large sum of cash, whether you’ve bought a ticket or not. Scammers will often try to coax you into giving away important information or money before you can claim your winnings in these types of scams.
Impersonation scams
Impersonation takes many forms – you might find someone catfishing on a dating website, or receive an email from someone pretending to be your boss. These scams will attempt to be someone else to get you to do something, like clicking a link or transferring money, that puts your funds or data at risk. This can also involve impersonating well-known figures like celebrities or politicians, or even hit an emotional point by pretending to be a family member in need.
Scams in Australia: how to stay safe

How to protect yourself
Scams can target anyone, but there are some measures you can take to minimise the risk of falling for one.
- Update your privacy settings for any online accounts, including social media
This can stop scammers from getting access to personal contact information such as emails or phone numbers. Additionally, it can help to prevent bad actors from using your information to scam others, as some scammers will create entire false profiles using information they’ve stolen off social media in an attempt to trick others who might know you.
- Examine links before you click
Be critical of any suspicious links in emails and texts, or unknown phone numbers which attempt to contact you, especially when the contact is unexpected. In a phishing attempt, scammers will often include malicious links to get you to hand over personal data. Check spelling in the URL, and look out for any out-of-place characters. See if links you’ve been sent match what appears when you Google the organisation's name.
- Keep your devices up-to-date
Keeping your device's softwares up-to-date can help to filter out unwanted calls, texts or emails thanks to spam filters that can stop potentially harmful communications from coming through. Brands like Microsoft, Apple and Google are constantly adding in new security features, while also reducing support for older software, meaning that an outdated web browser, for example, might be more prone to viruses and malware. Having one of the best antivirus software installed, or one of the best VPNs can also help to secure your PC on the chance that someone clicks a scam link.
- Have strong and secure passwords
Make sure your passwords are strong and secure, and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) when you can. This will help stop scammers, especially if they’re attempting to access any of your accounts remotely. Best practice is to make sure you have a separate password for each and every account, and there’s password managers available to help stop you from forgetting them. Passphrases are more difficult to guess than passwords, and the Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) has a helpful guide for creating passphrases.
- Be cautious when shopping online
When making purchases online, you can prevent scams from taking your money by using payment methods with inbuilt security measures. Some methods include using a credit card, or PayPal, which has a buyer protection policy, plus some online marketplaces also have safeguards like eBay’s Money Back Guarantee or Amazon’s A-to-Z Guarantee.
- Stay in the know
Keeping informed about scams is the best way to stay protected. It’s unlikely that you’ll be able to filter out all possible scams and you’d basically have to go off grid to avoid most of them. Even then, old-fashioned scammers can still target people in person. If you know what to look for, you’ll be ahead of any scammer and also able keep your family and friends aware of any happening right now – they might be in a more vulnerable position to fall for a scam, particularly if they’re not tech-savvy, and scammers prey on vulnerabilities to get what they want.
How to spot a scam
While scammers are constantly finding new ways to mislead someone, there’s a few ways to spot a scam:
- Look for suspicious URLs that contain spelling errors or incorrect domains. You can use ICANN Lookup to verify if a web address is legitimate or not.
- Double check any email addresses – phishing emails will often have an error with the email address, such as the domain not matching the sender’s company.
- Random numbers are often spoofed for scam calls and texts – you can search numbers on the internet to see if they've been used in scams previously.
- Photos or videos of celebrities and politicians used out of context with some outrageous claim are often scams, and you can use reverse image search engines like TinEye to find the original source.
- Deepfakes can also be spotted by looking at the details – a video might be really low quality to hide imperfections, or an image might have strange shadows or unrealistic features.
What to do if you get scammed
It’s easy to fall victim to a scam – it’s pretty likely that most of us will at least come close to it at some point in our lives. If you find yourself in this position, there are some things you can do to minimise financial loss and harm:
- Secure your data and finances
If you’ve lost money in a scam, or the scammer has gained access to any bank accounts (or you just suspect they have), you’ll want to contact your financial institution as soon as possible. If you’ve made a payment through a credit card or via PayPal, there’s safeguards in place to help get your money back. Other methods such as PayID and bank transfers might have a few more hoops to jump through with no guaranteed success, but you should be able to at least lock any accounts to prevent further loss.
You’ll also want to look into securing any compromised accounts. This can be as simple as changing your passwords, and you can check Have I Been Pwned? to see if any emails or passwords have been leaked. You also might want to consider setting up two-factor authentication to prevent any further unwanted sign-ins.
- Contact the authorities
Immediately after contacting your bank or financial institution, you should get in touch with a governing body that specialises in scams. These places will have resources to help you minimise any potential loss and report it.
If you’ve been targeted by a scammer but you haven’t handed over any money or personal details, report it to Scamwatch. If you’ve lost money or had your personal details stolen by a scammer, report it to ReportCyber. More details for reporting and recovering from scams are available on the Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) website.
Here’s a list of websites with contacts and resources to help support you if you’ve been scammed:
- Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC)
- Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) - Scams
- Crime Stoppers
- Money Smart: what to do if you've been scammed
- Scamwatch
Reporting a scam can also help these institutions to spread awareness about scams, hopefully preventing others from falling victim in the future.
If you’re concerned about your identity being compromised due to a scam, IDCARE is a support service that has resources and the ability to help you make your identity secure again after being scammed.
Additionally, you might want to contact any companies where your accounts have been compromised. Big telcos such as Telstra and Optus have resources to help customers in the event of a scam, including dedicated spaces to keep track of current scams and how to report them. Additionally, Optus also has a dedicated resource for current customers in Optus ScamWise, which offers more in-depth information, such as how many scam texts and calls Optus is blocking on a weekly basis.
If you’ve fallen for a scam at work, such as a phishing email, you’ll want to let your workplace’s IT department know as soon as possible.
- Seek support from family, friends and professionals
Being scammed can do a number on your wellbeing, so it’s important to lean into your support group while you navigate this situation. If you can, talk to someone you feel comfortable with, and reach out to professionals such as therapists and counsellors who can help you navigate any emotions or feelings you have during this time.
Anti-scam resource kit
Here’s some resources to help spot and prevent scams, as well as places to report any that you might come across. We’ve also tracked down some resources to help reduce any losses if you have fallen for a scam, plus some further reading on scams from trusted sources.
Prevention
- ABN Lookup: check business numbers against the ABN database
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission: check if a someone is registered to give financial advice
- Australian Signals Directorate: tips on creating secure passphrases
- Avast: antivirus software suites and free ransomware decryptor
- eSafety Commissioner: advice for securing emails, social media and other online interactions
- ICANN Lookup: verify URLs and website domains
- Bitdefender: antivirus and free ransomware decryptor
- PayPal: alternative online payment method with buyer protection
- TinEye: reverse image search
- Whois lookup: check website domains for legitimacy
Reporting
If there is immediate danger regarding a scam, you can call 000. Otherwise, report directly to the police on your local non-emergency line, and/or through the following resources:
- Australian Cyber Security Hotline: 1300 292 371
- Australian Federal Police: report a crime online directly to the Federal Police
- Australian Signals Directorate: ways to report cybercrime for businesses, organisations and individuals
- Crime Stoppers: report directly on the website or call 1800 333 000
- Scamwatch: report suspicious activity to help prevent others from being scammed
Mitigation
- Beyond Blue: emotional support online or call 1300 22 4636
- Have I Been Pwned: check passwords and emails for data breaches
- IDCare: assistance to help secure your identity
- Lifeline: online or call 13 11 14 for counselling if you’re feeling distressed
- Money Smart: tips to help prevent further financial loss
Further information
- Australian Competition and Consumer Commission: scam data, reports and resources available through Scamwatch

Zac was part of TechRadar's Australian phones desk, covering the big releases from the likes of Google, Samsung and Apple. He continues to write about the Aussie EV market for this publication. He's previously written for Gizmodo Australia, Canstar Blue and The Daily Mail Australia (with articles on Nine, Junkee, Kotaku Australia and Lifehacker Australia).
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.