Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The Windows Command Prompt is powerful yet often overlooked. It harks back to the days of DOS and the command-line, and continued to feature in early versions of Windows.
Over time, it's been forced into the background, as Microsoft has pushed bells and whistles, but the Command Prompt has never been ignored, and continues to play a big role, particularly when troubleshooting.
The big headlines may have gone to the new Windows 10 user interface, or some of its more crowd-pleasing features, but the Command Prompt is still nurtured by the Microsoft boffins, and Windows 10 introduced a number of handy improvements to the console window, making it more accessible and easy to use.
New tricks
You can now resize the console window more easily, simply through drag-and-drop – no more messing about with console buffer size settings (although you still can, if you prefer).
Word wrap means text doesn't get lost off-screen, forcing you to horizontally scroll to read particularly long lines of text. You can now easily select parts of the console output with your mouse, and copy them to the clipboard with just one click (or, more precisely, one right-click).
There are even useful new text-selection key combinations, which helps speed things up further, too. But even without these features, the Command Prompt remains a powerful and vital tool in any self-respecting PC user's armoury. So why let Linux have all the fun with its Terminal, when you can give your computer some command-line attention in Windows, too?
Join us as we dissect the Command Prompt, and reveal how to best use it.
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
System File Checker
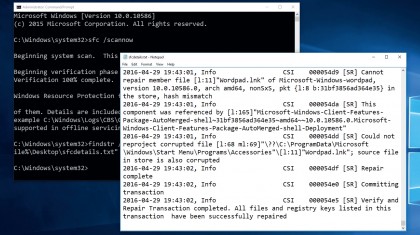
One of the best-known Command Prompt tools is System File Checker (SFC), and most know that typing sfc / scannow should, in theory, detect corrupt system files and replace them with working backups. But, it's not always successful – if you get a message telling you Windows Resource Protection was unable to fix the files it found, try the following.
First, generate a text file with the information required to track down the files SFC couldn't fix:
findstr /c:"[SR]" %windir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log "%userprofi le%\Desktop\sfcdetails.txt"
Now open the sfcdetails.txt file – this is a filtered view of the CBS.log, containing only the files SFC couldn't fix. Identify the corrupt files, and source working versions from another PC running the same version of Windows. Now issue the following commands for each corrupt file, replacing path with the file's path (such as C:\Windows\System32), and corruptfile with its full filename (jscript.dll):
takeown /f path \ corruptfile icacls path \ corruptfile /
GRANT ADMINISTRATORS:F
Copy the file you took from the other PC into the same folder, overwriting when prompted:
copy sourcepath \ sourcefile
path \ corruptfile
Run SFC again, which should now verify there are no corrupt files. For more, see Microsoft's Support page on the subject.
Customise the Command Prompt
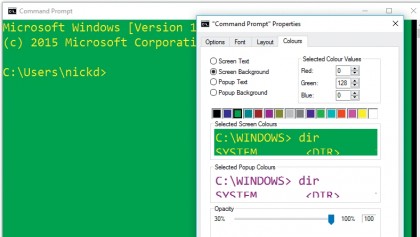
Before delving too deep into the Command Prompt utility, make sure you take the time to customise its appearance to your personal comfort.
To do this, right-click the Command Prompt icon on its menu bar, and choose 'Properties'. You'll see options spread out over four tabs: 'Font' controls the text type, size and style, while 'Colors' lets you change the background and text colours, plus make the window semi-transparent.
The 'Layout' tab enables you to set the window size in lines (height) and text characters (width), while the Screen Buffer Size height reveals how many lines you can scroll through. The default size should be suffi cient – make sure you leave the 'Wrap text output on resize' option ticked.
The main tab – 'Options' – enables you to tweak the command buffer (this is basically your command 'history', and you can cycle through previous commands using the up cursor key). You can also change the mouse cursor size, plus enable or disable various features, many of which are new to Windows 10, such as the ability to copy and paste selected text using the keyboard ('Enable Ctrl key shortcuts').
If you're resolutely old-school and like things as they are, you can tick 'Use legacy console', and do without these feature improvements, but in the majority of cases, we suggest leaving well alone.