Microsoft shows why Windows 11 needs TPM – even if some PCs are left out in the cold
Real life hack scenarios are demonstrated in a video clip
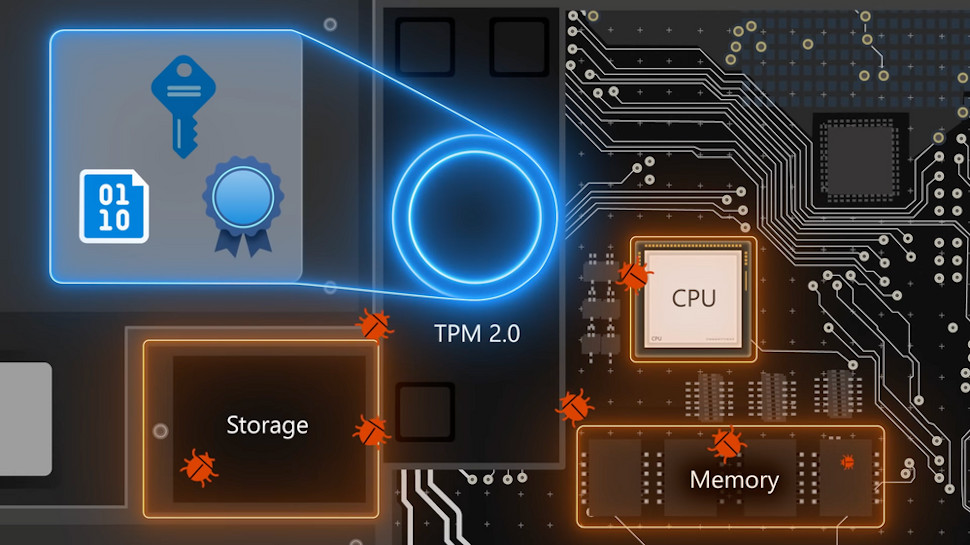
Windows 11 security is something of a hot topic, as the revamped OS comes with much tighter defenses than Windows 10, but with the side-effect of creating controversy and confusion on the system requirements front (and indeed for gamers – more on that later).
However, Microsoft recently produced a video to show how Windows 11’s new protective measures – which include TPM (Trusted Platform Module), Secure Boot and VBS (Virtualization-Based Security) – help to make systems safer against hackers. Furthermore, it reminds us these moves are an extension of what was already happening with Windows 10 (but crucially, not on a compulsory level).
- Download the best Windows 10 antivirus
- Check out all the best PC games
- We'll show you how to build a PC
The clip stars Microsoft’s security expert Dave Weston who explains more about why this higher level of security, which entails the aforementioned raised hardware requirements – including support for TPM 2.0, which rules out a fair number of not-all-that-old PCs – is required to defend against some potentially nasty security breaches.
Weston shows how this nastiness could play out in real world situations, first of all demonstrating a remote attack leveraging an open RDP (remote desktop protocol) port, brute forcing the password, and then infecting the machine with ransomware. This was on a PC without TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot, and naturally, wouldn’t be possible on a Windows 11 system.
The second attack used for demo purposes is an in-person one using a PCI Leech device to access system memory and bypass fingerprint recognition to login. VBS stops this kind of attack being leveraged against a Windows 11 system, and the former remote attack is prevented by UEFI, Secure Boot and Trusted Boot (in conjunction with TPM).
Analysis: Land of confusion
This is an interesting look at the nuts-and-bolts of how these security countermeasures work against real life attacks. Clearly, in some scenarios there are good reasons for mandating TPM and the other mentioned security technologies to help keep a PC safer against a possible attack, whether that’s a remote or local intrusion.
No one is going to argue against better protection, but the issue with making these pieces of security tech a compulsory part of the system requirements is the confusion around whether or not a PC has these capabilities.
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
In some cases, newer machines do indeed have TPM on-board, it just isn’t enabled – leading to a frustrating situation where the owner of a modern device could be told it isn’t compatible with Windows 11. And while it might just be a case of switching TPM on, which isn’t difficult for a reasonably tech-savvy person, it could be very intimidating for a novice user (involving a trip to the BIOS, a scary place for the untrained eye).
VBS or Virtualization-Based Security has run into further controversy, as well, given that while this isn’t an issue for upgraders from Windows 10, it will be enabled by default on new PCs that come with Windows 11 – and it causes slowdown with gaming frame rates. By all accounts, VBS can be a pretty serious headwind for frame rates, too; and again, this adds to the confusion around what’s going on with Windows 11 machines in general.
Having a more secure PC is great, without a doubt, but there are costs here which have a potentially negative impact on the experience of some users adopting (or trying to adopt) Windows 11.
Via Neowin
Darren is a freelancer writing news and features for TechRadar (and occasionally T3) across a broad range of computing topics including CPUs, GPUs, various other hardware, VPNs, antivirus and more. He has written about tech for the best part of three decades, and writes books in his spare time (his debut novel - 'I Know What You Did Last Supper' - was published by Hachette UK in 2013).
