Five steps to keep your Android phone secure
Android might be free but some things about it should be locked up

Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
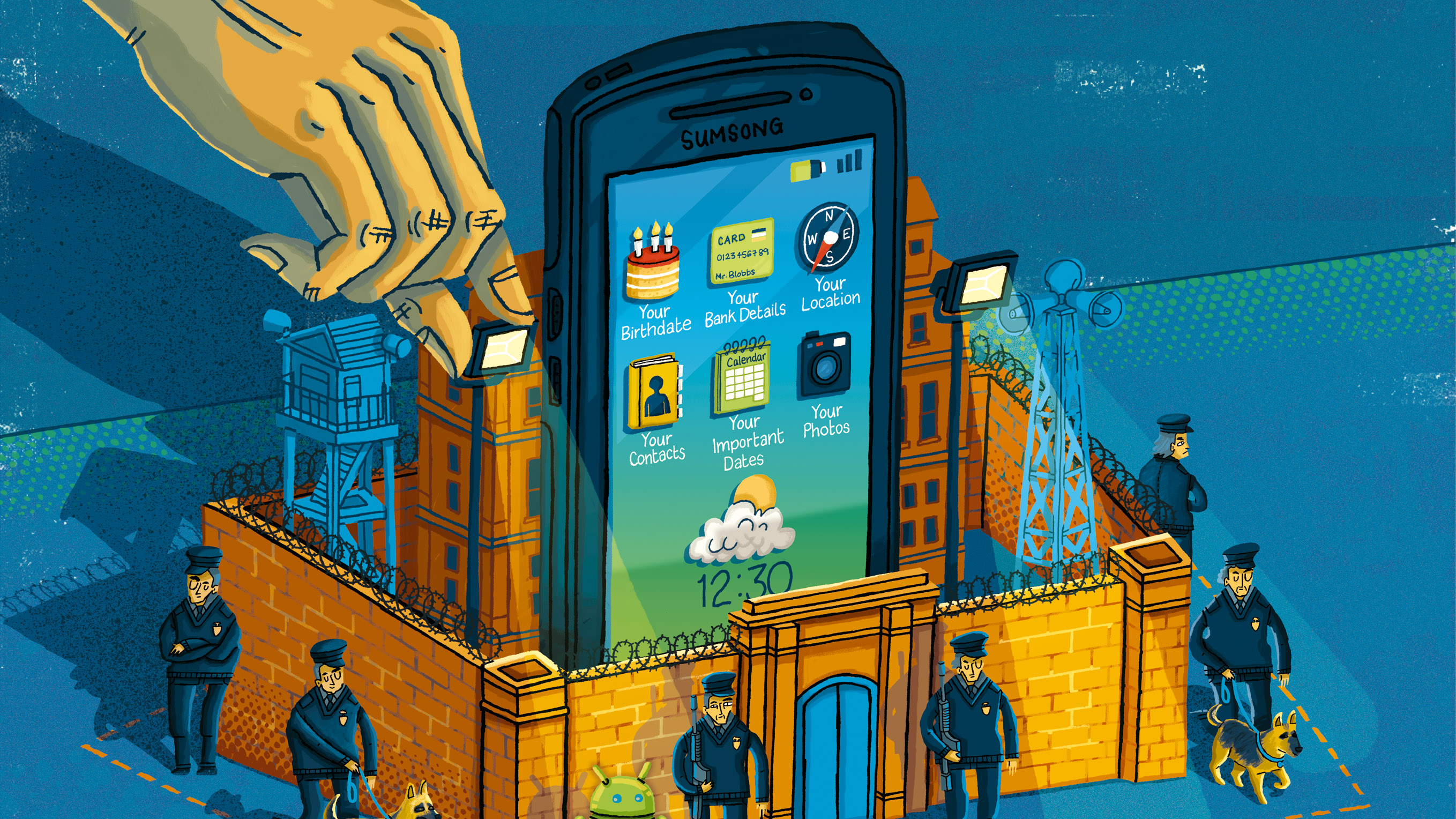
You have in your pockets a snooper's best friend. You take it everywhere: from your office to your bedroom, from the dining room to the lavatory (and hopefully clean it after). It records almost everything you do and can be made to turn against you in a matter of minutes. Believe it or not, the modern day smartphone is a private citizen's worst privacy nightmare.
Think about what you have in there: email addresses and phone numbers from your contacts, calendar appointments, photos, and probably even personal financial information. On top of that, smartphones can continually track your location to build a detailed profile of your whereabouts.
But just because it can doesn't mean you have to let it. Here's five simple steps you can take to control your smartphone security and keep your data, and life, private:
1. Manage your apps
To enjoy all the conveniences of a smartphone you need apps. Unfortunately, apps are the weakest link between your private data and the world. Many access your personal data to 'enhance their experience', leaving you to trust that they will only use this data in a desirable way. Unfortunately, not every app clearly states how they use this information. But there are ways to find out what your app knows about you and to restrict them.
A critical component of your Android smartphone is the permissions system. When you install an app, it notifies you of what it would like to gain access to. You can then install the app, or not. Unfortunately, this system puts a lot of responsibility on the users to know whether these access requests are appropriate.
Fortunately there are multiple ways of visualising app permissions. BitDefender's free Clueful will scan your apps and categorise them as high risk, moderate risk, and low risk. You can then browse each list and click on an app to find out the features it can access. You should uninstall any High Risk apps as they might be pinching your passwords or reading emails.
There's also Malwarebytes' Anti-Malware mobile app, which scans apps and divides them into categories based on the phone feature they have access to, such as your calendar or contacts, giving you full transparency on what your apps are up to.
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
2. Protect yourself online
In addition to preventing apps from leaking info, you should also minimise the personal data you put out there, even when sharing something as innocuous as images.
Images can reveal a lot of information about you thanks to the exchangeable image file format (EXIF) data attached to them. If you take an image with a GPS-enabled camera or a smartphone it can reveal your location, the time it was taken, as well as the unique ID of the device.
To strip EXIF information from pictures before sharing them you can use Instant EXIF Remover. This app doesn't have an interface, instead once installed it'll be available as an option in the 'Share' action. When selected, the app will intercept any images you wish to share and delete all EXIF data, before passing them on to the email client or any other sharing app.

After securing your images it's time to take control of your web browsing activities. Just like any desktop web browser you can install a variety of add-ons to your Android browser.
The Phony add-on can be used to customise the user-agent on the browser and hide the fact that you are on a mobile device. Then there's Self-Destructing Cookies add-on, which will automatically delete all cookies when you close a site.
For more comprehensive control you can use the CleanQuit add-on, which removes all information about the previous session including the browsing & download history and site preferences.
If you want full anonymity, you should switch to the Orweb browser. It's loaded with plugins to disguise your device, gives you control over cookies, prevents loading of Flash content and keeps no browsing history. However, it requires the Orbot plugin and Orbot is Tor for Android, which may not be something you wish to install.

With almost two decades of writing and reporting on Linux, Mayank Sharma would like everyone to think he’s TechRadar Pro’s expert on the topic. Of course, he’s just as interested in other computing topics, particularly cybersecurity, cloud, containers, and coding.