What is a motherboard: your computer's foundation explained
If you've ever asked 'what is a motherboard?', we've got you covered

Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
If you’ve ever looked inside a computer, you might have looked at the big square of plastic and circuits and asked ‘what is a motherboard and what does it do?’
Despite how it might look, it’s much more than a fancy piece of plastic that holds all of the various components of a computer together like the best processors, best graphics cards, and best SSDs.
Often hidden beneath a tangle of cables and components, the motherboard is the central hub that brings together all of the computer’s components and allows them to communicate with each other seamlessly so that all of a computer’s parts can function as one unit.
But before you can go shopping for the best motherboard to upgrade your PC, it helps to know more about it and what the right — and wrong — motherboard means for you and your PC.
In addition to providing lines of communication between different add-in components like the best RAM, the motherboard also houses essential circuits, chips, sockets, slots, and ports that determine the performance, expandability, and compatibility of your computer system, as well as regulating the power from your power supply unit to everything else in the PC to make sure everything operates safely.
There also isn’t just one kind of motherboard either, and each motherboard brings its own set of features and specifications, catering to various user needs from casual home users to hardcore gamers and content creators.
The motherboard truly serves as the backbone of your computer, dictating its performance, upgradability, and overall user experience, but it’s also one of the most opaque components in your computer, so you can be forgiven if the alphabet soup of model numbers, chipsets, and manufacturers leaves you rather bewildered. Fortunately, I’ve been covering computer hardware for years now (in addition to nearly a decade of academic work in computer science), and I’m here to help you navigate all these questions and more.
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
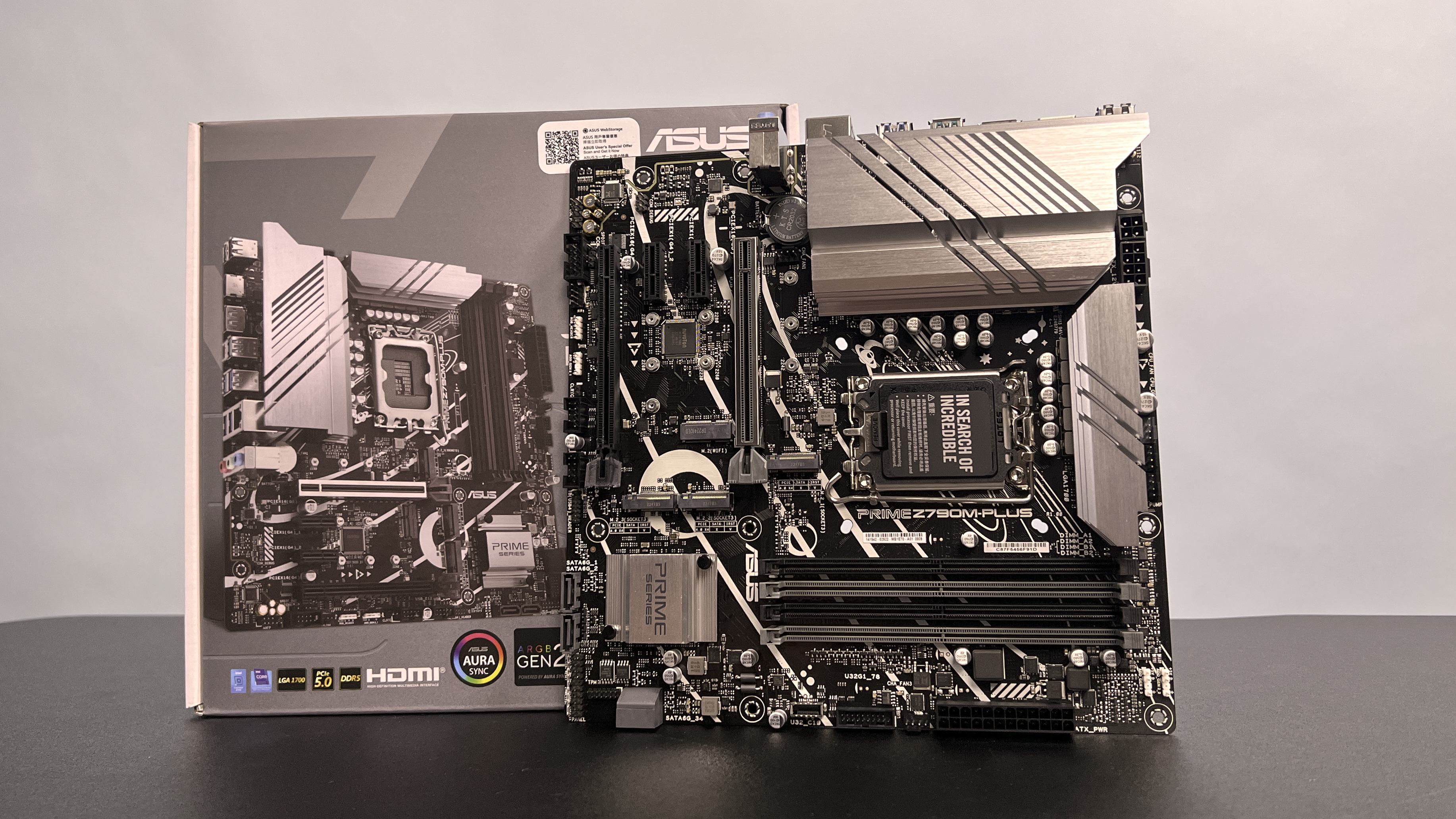
What is a motherboard?
What is a motherboard?
A motherboard, also known as a mainboard, system board, or logic board, is the primary circuit board found in computers and other electronic devices like smartphones.
It serves as a central hub that connects various components together, such as memory, storage, and your processor, allowing them to communicate and work together to enable the functionality of the system.
The motherboard provides electrical and mechanical support for essential components such as the CPU (Central Processing Unit), RAM (Random Access Memory), storage devices (such as hard drives and SSDs), expansion cards (like graphics cards and sound cards), and other peripherals. It acts as a platform for these components to be securely attached and interconnects them through various circuitry, slots, and ports.

What are a motherboard's key features and components
What are the key features and components of a motherboard?
There are several major components of a motherboard that are important to understand if you’re in the market for a new motherboard.
First, the CPU socket is a specific slot on the motherboard where the processor is installed. It provides the electrical connection and interface for the CPU to communicate with other components.
Next, you have RAM memory slots that accommodate the system memory modules, such as the best DDR5 RAM, allowing the CPU to access working proram data quickly.
Expansion slots are used to install expansion cards, which can include graphics cards, sound cards, network cards, or other peripheral cards. Expansion slots use various interfaces such as PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) or older standards like PCI or AGP, though you won’t really see the latter two on consumer motherboards much anymore.
The motherboard also has connectors for attaching storage devices such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). Common types include SATA (Serial ATA) ports for traditional drives and M.2 slots for high-speed NVMe SSDs.
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or its successor, the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI), is stored on a chip on the motherboard. It provides firmware-level instructions and settings for initializing the hardware and booting the operating system.
The motherboard has power connectors for receiving electrical power from the PSU (Power Supply Unit), as well as electrical connectors for components like CPU coolers to receive power through the motherboard. These also include the main 24-pin ATX connector and auxiliary connectors like the 4-pin or 8-pin CPU power connector.
The motherboard also provides various ports and connectors for attaching peripherals, including USB ports, audio jacks, Ethernet ports, video output ports (such as HDMI, DisplayPort, or VGA), and more.
These are just some of the essential features and components found on a motherboard. Different motherboard models and form factors may have additional or varying features based on their intended use, such as gaming, content creation, or server applications.
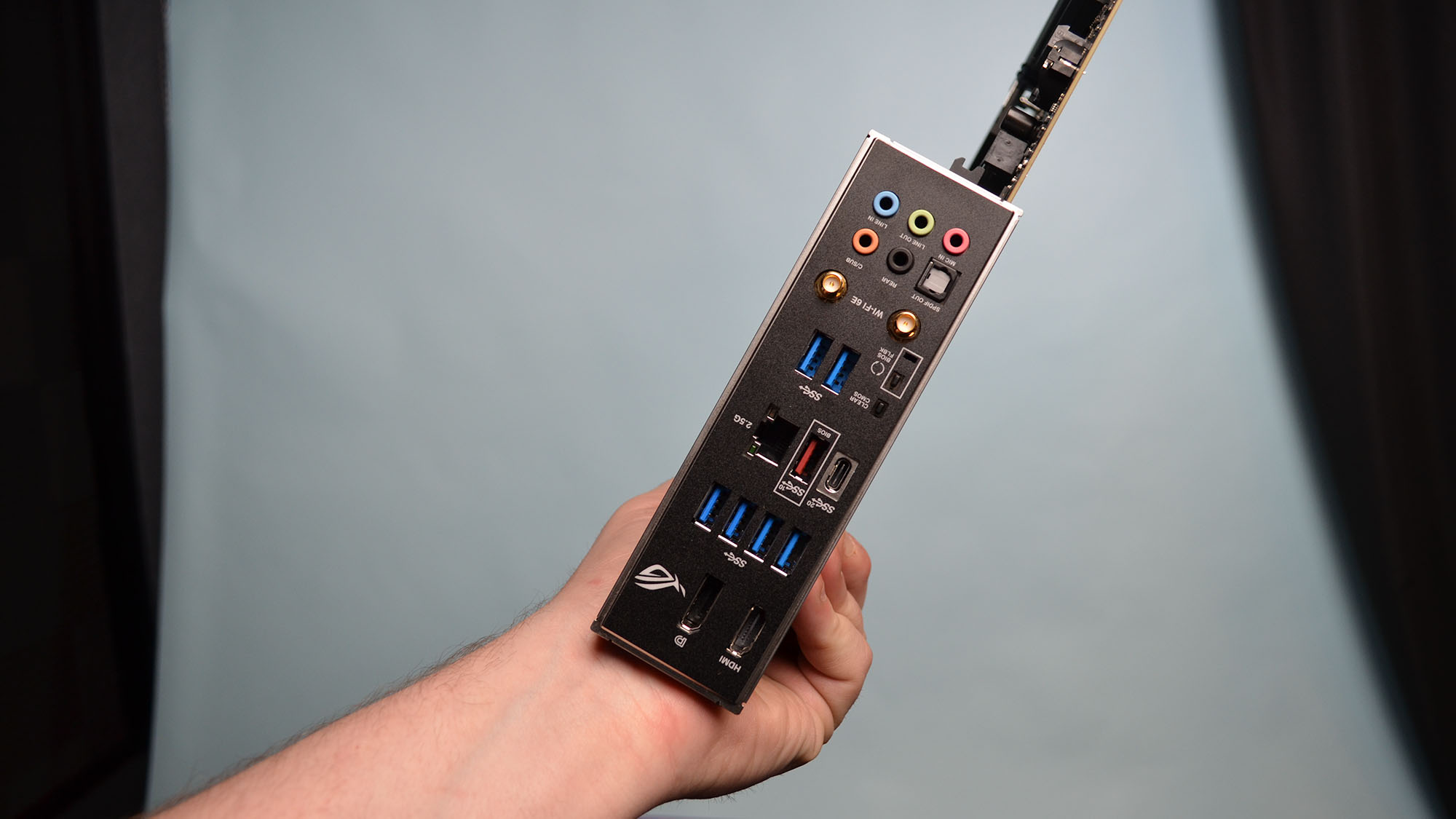

What are the functions of the motherboard?
What are the functions of the motherboard?
The motherboard plays several critical functions in a computer system.
First and foremost, the motherboard serves as a central platform that allows different components to connect and communicate with each other.
The motherboard’s second most important function is power delivery to the various components connected to it. The motherboard distributes power from the PSU to the various components, as well as voltage regulators that ensure that components don’t get overloaded or experience power spikes that could damage them.
The motherboard also facilitates the transfer of data between different components using special circuits called buses and interfaces that allow data to flow between the CPU, RAM, storage devices, expansion cards, and other peripherals. These interfaces may include SATA, USB, PCIe, Ethernet, and audio interfaces, among others.
The BIOS or UEFI chip on the motherboard contains the necessary firmware to provide instructions and settings for initializing the computer’s hardware during the system's startup. It performs tasks such as the Power-On Self-Test (POST), which checks the system's hardware, and provides a basic set of instructions for booting the operating system.
Finally, the motherboard generates clock signals that synchronize the operations of different components so that everything works in an orderly fashion, much like a traffic light keeps traffic flowing smoothly. Clock signals ensure that data transfer, processing, and other operations occur at the correct timing, preventing data errors and enabling proper coordination between components that prevents cascading bottlenecks that can potentially cause your computer to “freeze”..
Overall, the motherboard acts as the foundation of a computer system, facilitating communication, power distribution, data transfer, and coordination among all the components, ultimately enabling the system to function as more than just the sum of its components.
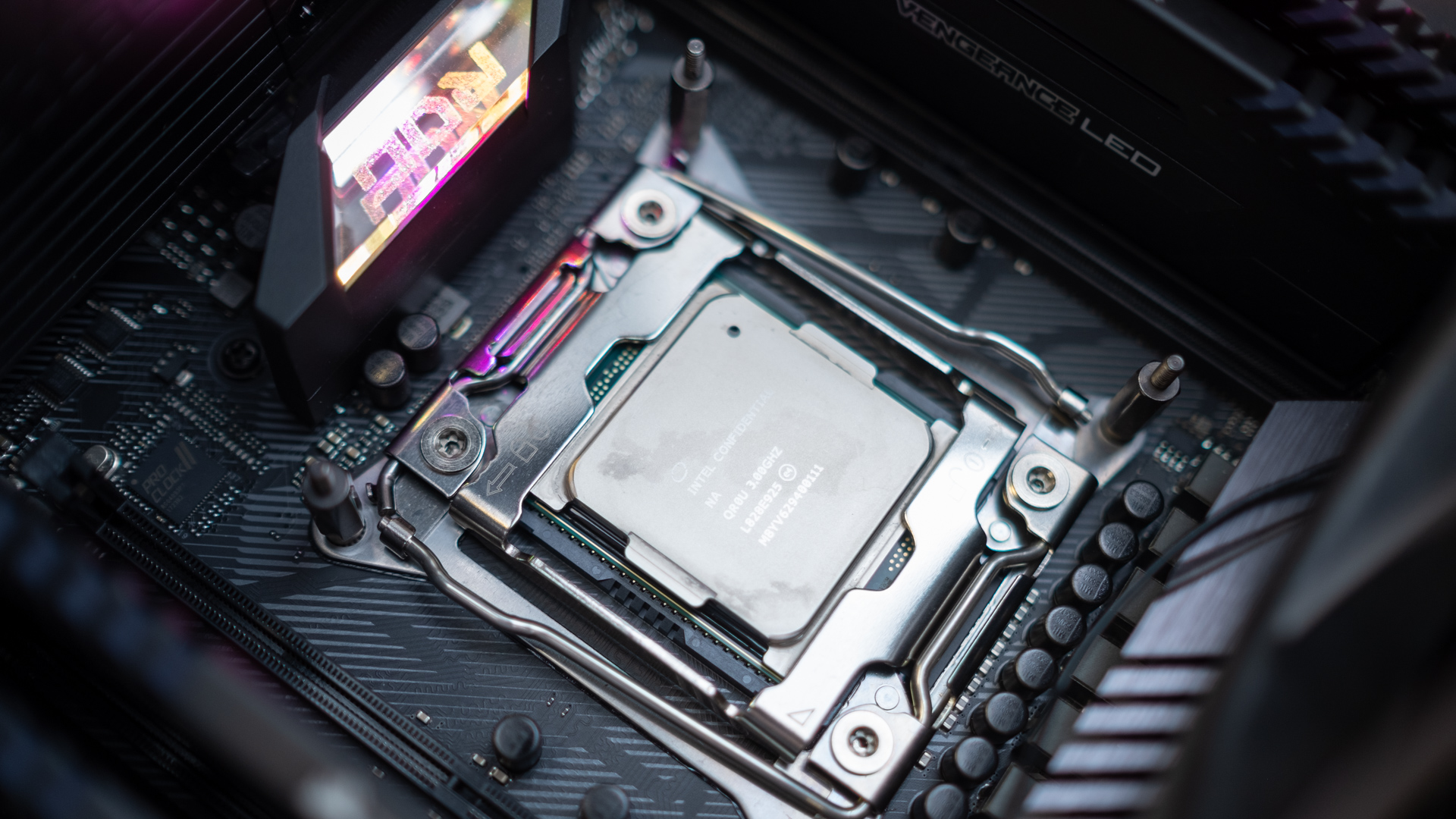

What is the difference between a CPU and a motherboard?
What is the difference between a CPU and a motherboard?
The CPU and motherboard are two distinct components in a computer system that serve different functions.
The CPU is often referred to as the "brain" of the computer. It is responsible for executing instructions, performing calculations, and controlling the overall operation of the system. The CPU is a microprocessor that handles the majority of the computational tasks in a computer. It consists of the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), control unit, and cache memory.
The motherboard contains several key elements such as the CPU socket, RAM slots, expansion slots, storage connectors, power connectors, and input/output ports but doesn’t carry out any instructions itself.
It is simply the bridge over which your PC’s components can communicate and collaborate with one another safely and efficiently.
Do you need a motherboard in a PC?
Do you need a motherboard in a PC?
Yes, a motherboard is an essential component in a PC, just as a skeleton is necessary for the human body to function.
Without it, every PC component would need to have independent connections to other components it might need to work with to carry out a given task, and without a motherboard, these components would also be at the mercy of dangerous power fluctuations that can damage the circuitry inside them.
Today's best motherboard deals

John (He/Him) is the Components Editor here at TechRadar and he is also a programmer, gamer, activist, and Brooklyn College alum currently living in Brooklyn, NY.
Named by the CTA as a CES 2020 Media Trailblazer for his science and technology reporting, John specializes in all areas of computer science, including industry news, hardware reviews, PC gaming, as well as general science writing and the social impact of the tech industry.
You can find him online on Bluesky @johnloeffler.bsky.social