10 technologies that really could change the world
Phone tracking, biohacking and alternatives to fracking
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
8. Serious solar
Solar technology has been held back by several issues: solar panels are hefty, pricey, and of course they don't provide energy when it's dark. The biggest problem, though, is efficiency: as National Geographic reports, they only capture 10 to 20 percent of the sunlight that strikes them.
The future? Nanotech that makes the panels much less reflective, much cheaper to produce and much more efficient. Other ideas include tiny antennae on devices that capture solar energy and instantly convert it to power, solar panels that can actually store energy, and nanotech paint that turns entire buildings into solar energy collectors.

9. Biohacking
There's a controversy brewing on Kickstarter: the Glowing Plant project plans to engineer glow-in-the-dark plants, and some experts are worried: they fear that this is the thin end of a very big and scary wedge.
Article continues belowAs Nature reports, "they fear that distributing the plants could set a precedent for unsupervised releases of synthetic organisms, and might foster a negative public perception of synthetic biology - an emerging experimental discipline that involves genetically engineering organisms to do useful tasks."
Biohackers could engineer entirely new lifeforms, good or bad, and the emerging sector is almost entirely unregulated. Friends of the Earth has called for a global moratorium on the release of synthetic organisms "until the proper regulations and safety mechanisms have been put in place".
10. Genetic scanning
The MyGenome iPad app is a glimpse of the future, enabling you to analyse the full genetic makeup of someone. For now that someone is the developers' CEO, but if DNA sequencing prices continue to plummet - the cost per person has dropped from US$2.7 billion to US$5,000 in ten years - then full genome analysis could be in many of our futures.
That could have profound implications: we could discover if we're prone to particular kinds of cancer, or if we have higher than average risks of various unpleasant conditions, or if particular drugs could kill rather than cure us.
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
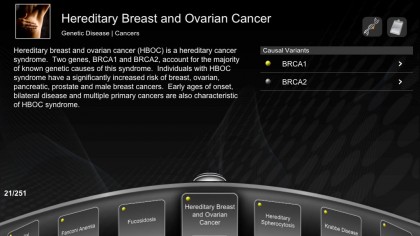
Angelina Jolie's recent preventive surgery was an example of DNA sequencing in action: Jolie has the BRCA1 gene, which means she has a high risk of developing the breast cancer that killed her mother.
As Carole Cadwalladr writes in The Guardian: "revealing our full DNA will revolutionise medicine - but it will also raise huge ethical questions about what we do with the information".

Contributor
Writer, broadcaster, musician and kitchen gadget obsessive Carrie Marshall has been writing about tech since 1998, contributing sage advice and odd opinions to all kinds of magazines and websites as well as writing more than twenty books. Her latest, a love letter to music titled Small Town Joy, is on sale now. She is the singer in spectacularly obscure Glaswegian rock band Unquiet Mind.