What is an NPU: the new AI chips explained
What is an NPU? Possibly the biggest advance in computing in a generation
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
If you've been paying attention to Intel, AMD, or Apple in recent weeks, you may have been asking 'what is an NPU and why do I need one?'
To many consumers, a computer simply has a processor and that's it, but the reality was already a bit more complicated than that. Now, thanks to new processor advances from Intel and AMD, it's about to get even more so.
Fortunately, you don't have to fend for yourself if you're shopping for a new Intel or AMD laptop with these new-fangled chips that claim to be heralding a new era of AI PCs. It's not as complex as it might seem, at least as far as you need to be concerned when looking to buy one of the best laptops on the market this year.
I'm here to walk you through everything you need to know about these new neural processing units and how they're going to help you with a whole new range of AI-accelerated tasks, from productivity to gaming.
What is an NPU?
What is an NPU?
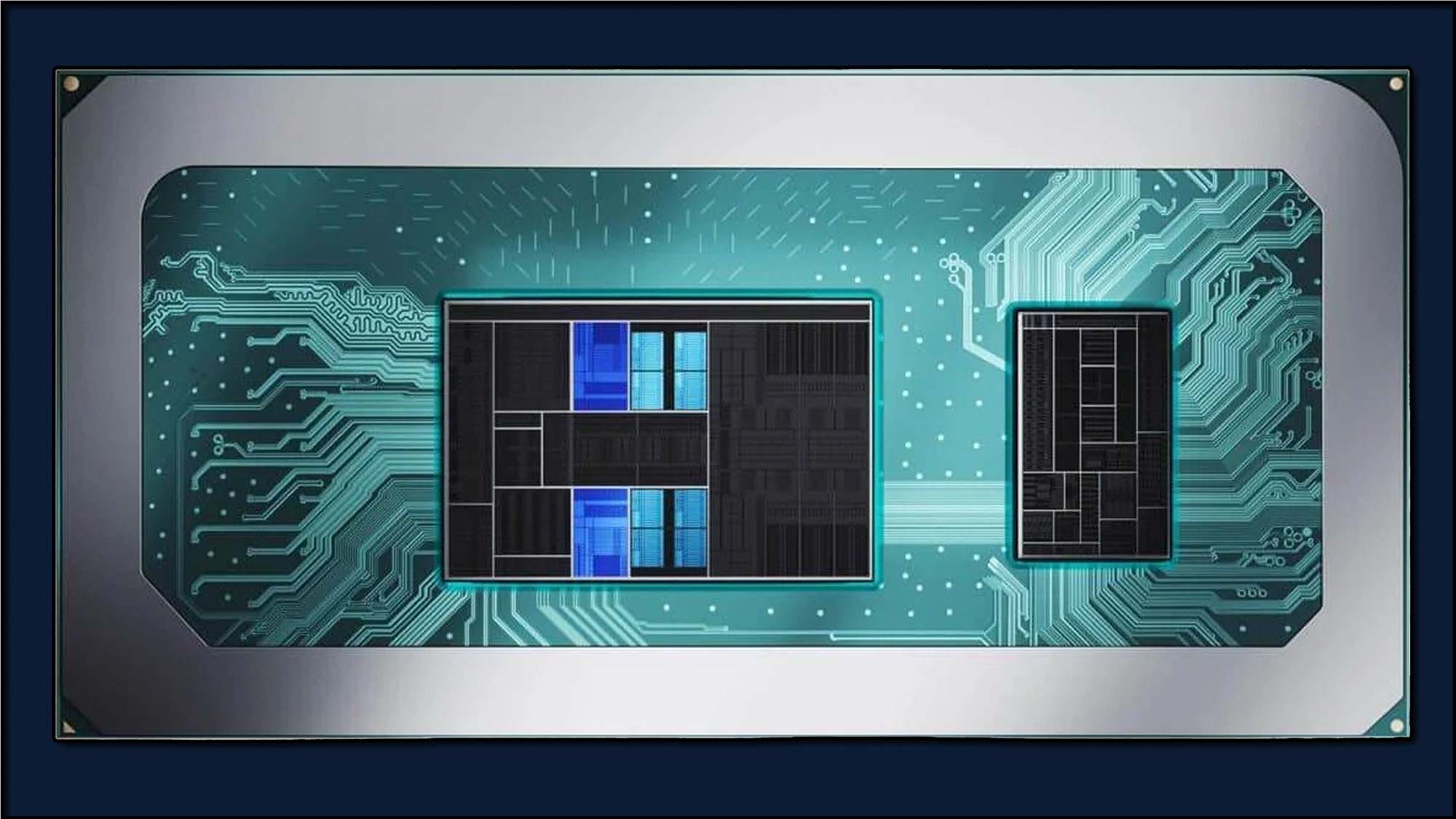
An NPU, or Neural Processing Unit, is a dedicated processor or processing unit on a larger SoC designed specifically for accelerating neural network operations and AI tasks. Unlike general-purpose CPUs and GPUs, NPUs are optimized for a data-driven parallel computing, making them highly efficient at processing massive multimedia data like videos and images and processing data for neural networks. They are particularly adept at handling AI-related tasks, such as speech recognition, background blurring in video calls, and photo or video editing processes like object detection.
NPUs are integrated circuits but they differ from single-function ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits). While ASICs are designed for a singular purpose (such as mining bitcoin), NPUs offer more complexity and flexibility, catering to the diverse demands of network computing. They achieve this through specialized programming in software or hardware, tailored to the unique requirements of neural network computations.
For most consumer products, the NPU will actually be integrated into the main CPU, as in the Intel Core and Core Ultra series or the new AMD Ryzen 8040-series laptop processors. At larger data centers or more specialized industrial operations, though, the NPU might be an entirely discrete processor on the motherboard, separate from any other processing units.

NPU vs. GPU
While many AI and machine learning workloads are run on GPUs, there is an important distinction between the GPU and NPU.
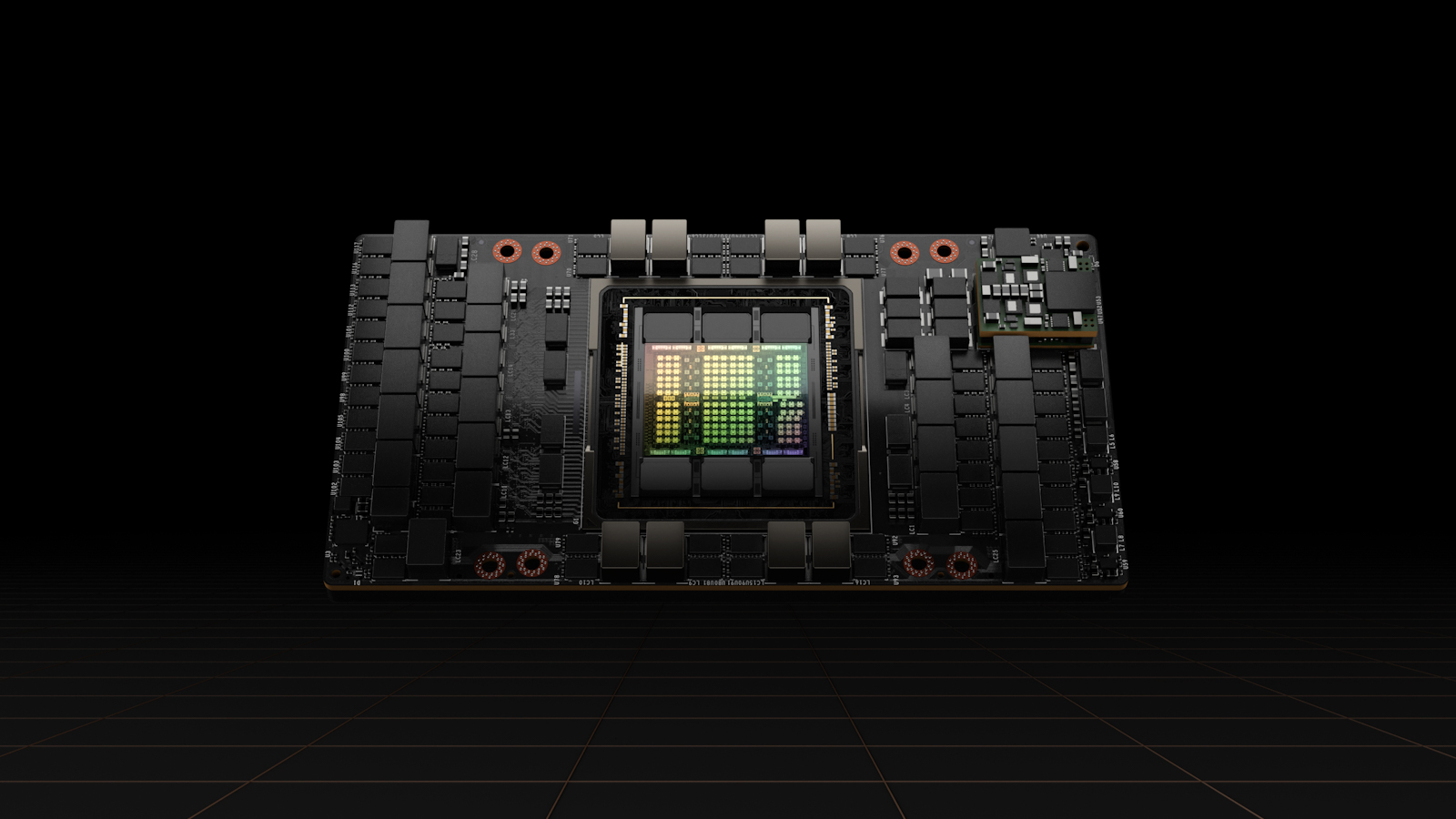
While GPUs are known for their parallel computing capabilities, not all GPUs are good at doing so beyond processing graphics, as they require special integrated circuits to effectively process machine learning workloads. The most popular Nvidia GPUs have these circuits in the form of Tensor cores, but AMD and Intel have also integrated these circuits into their GPUs as well, mainly for handling resolution upscaling operations — a very common AI workload.
NPUs, meanwhile, simply take those circuits out of a GPU (which does a bunch of other operations) and make it a dedicated unit on its own. This allows it to more efficiently process AI-related tasks at a lower power level, making them ideal for laptops, but also limits their potential for heavy-duty workloads that will still likely require a GPU to run.
The role of NPUs in different systems
NPUs are designed to complement the functions of CPUs and GPUs. While CPUs handle a broad range of tasks and GPUs excel in rendering detailed graphics, NPUs specialize in executing AI-driven tasks swiftly. This specialization ensures that no single processor gets overwhelmed, maintaining smooth operation across the system.
For instance, in video calls, an NPU can efficiently manage the task of blurring the background, freeing up the GPU to focus on more intensive tasks. Similarly, in photo or video editing, NPUs can handle object detection and other AI-related processes, enhancing the overall efficiency of the workflow.
NPUs in PCs
NPUs are becoming increasingly common in the PC and laptop domain. Intel's Core Ultra processors and Qualcomm's Snapdragon X Elite processors are examples where NPUs are integrated alongside CPUs and GPUs. These NPUs handle AI tasks faster, reducing the load on the other processors and leading to more efficient computer operations.
Qualcomm's NPU, for instance, can perform an impressive 75 Tera operations per second, showcasing its capability in handling generative AI imagery. This inclusion of NPUs in the latest generation of devices means that the industry is well-equipped to leverage the latest AI technologies, offering more AI-related conveniences and efficient processes for users.

NPUs in mobile devices
In smartphones, NPUs play a crucial role in AI computing and applications. Huawei was one of the first companies to integrate NPUs into smartphone CPUs, significantly enhancing AI arithmetic power and energy efficiency compared to traditional CPUs and GPUs. Apple's Bionic mobile chips have leveraged NPUs for tasks like video stabilization, photo correction, and more.
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
NPUs also enhance the capabilities of devices in recognizing content in photos, adjusting camera settings for optimal shots, creating bokeh effects in selfies, and aiding in AI-driven features like Bixby Vision on Samsung Galaxy devices.
NPUs in other devices
NPUs are becoming increasingly popular in a range of devices that traditionally haven't had advanced processors, like TVs and cameras. But as every electronic device becomes more and more of a computer in its own right, NPUs are finding their way into all sorts of devices around the home.
In TVs, for example, NPUs are used to upscale the resolution of older content to more modern 4K resolution. In cameras, NPUs can be used to produce image stabilization and quality improvement, as well as auto-focus, facial recognition, and more.
Smart home devices are also making use of NPUs to help process machine learning on edge devices for voice recognition or security information that many consumers won't want to be sent to a cloud data server for processing due to its sensitive nature.
The Future of NPUs
As we progress further into an increasingly AI-driven future, the growth of NPUs will only accelerate. With major players like Intel, AMD, and Qualcomm integrating NPUs into their latest processors, we are stepping into an era where AI processing is becoming more streamlined, efficient, and a whole lot more ubiquitous.
Devices equipped with NPUs will be able to perform AI tasks faster, leading to quicker data processing times and more convenience for users. Whether it's through faster video editing, advanced AI filters in applications, or efficient handling of AI tasks in smartphones, NPUs are paving the way for a smarter, more efficient computing experience.
In the end, NPUs represent a significant leap forward in the world of AI and machine learning at the consumer level. By specializing in neural network operations and AI tasks, NPUs alleviate the load on traditional CPUs and GPUs. This leads to more efficient computing systems overall, but also provides developers with a ready-made tool to leverage in new kinds of AI-driven software, like live video editing or document drafting. In essence, whatever task you're performing on your PC or mobile device, it's likely NPUs will eventually play a role in how those tasks are processed.

John (He/Him) is the Components Editor here at TechRadar and he is also a programmer, gamer, activist, and Brooklyn College alum currently living in Brooklyn, NY.
Named by the CTA as a CES 2020 Media Trailblazer for his science and technology reporting, John specializes in all areas of computer science, including industry news, hardware reviews, PC gaming, as well as general science writing and the social impact of the tech industry.
You can find him online on Bluesky @johnloeffler.bsky.social