52 Windows problems and solutions
Quick fixes for problems in XP, Vista and Windows 7
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
It's a sad fact of life that no Windows PC performs faultlessly over time. Many of these problems are outside your control, but others can be introduced through user error.
It doesn't matter how much simpler Microsoft makes Windows with each successive release: problems, glitches and bugs will always be a part of it.
Each month PC magazine from Future Publishing answer dozens of reader questions, so we've trawled our extensive archives and dug out 52 of the most relevant fixes to Windows problems.
Where possible we avoid referring to software that promises to fix these; these "miracle" cures often introduce problems of their own. Instead we try to concentrate on explaining how to fix various problems using only the tools in Windows itself.
01. Missing Taskbar icons
Version: XP, Vista, 7
If icons have disappeared from the Taskbar's notification area, there are two things to try: first, press the Windows key and [R], type "regedit" and press [Enter].
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
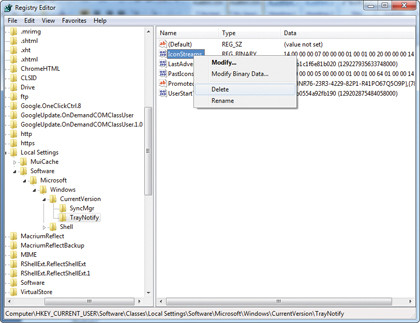
Browse to HKEY_CURRENT_USER\ Software\Classes\Local Settings\Software\Microsoft\Windows\ CurrentVersion\TrayNotify, and delete both IconStreams and PastIconsStream values.
Reboot, or log off and back on again. If the problem persists in XP, and you can live without it, open the Add or Remove Programs Control Panel, click Add/Remove Windows Components, expand Networking Services, and untick "UPnP User Interface". Then click OK > Next.
02. PC won't sleep
Version: XP, Vista, 7
If your PC won't stay asleep it's often because a device is configured to bring it out of standby when triggered. Identify the culprit by pressing the Windows key and [R], type "cmd" and press [Enter].
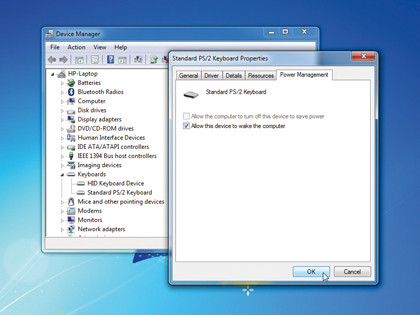
Type the following line and press [Enter]: powercfg –devicequery wake_armed
Now press the Windows key and [R] again, but this time type "devmgmt.msc" to open Device Manager. Find any devices listed earlier, then double-click them and look for an Advanced or Power Management tab.
Check if the device is allowed to bring the PC out of standby – if it is, untick all the boxes that wake it. Click OK, close Device Manager and test it worked; repeat the process if necessary.
03. Quick fixes
Version: XP, Vista, 7
Microsoft has developed the Fix It Center tool, which includes all of the automated fixes for various Windows problems it has released over the last few years. Download and install it from http:// fixitcenter.support.microsoft.com, then launch the tool from its desktop shortcut.
A list of available troubleshooters for your version of Windows will be listed; if one describes the problem you're having then click the Run button next to it and see if it can resolve your problem.
04. Remove printer drivers
Version: XP, Vista
To ensure all traces of an old printer are removed from your PC, open Printers or Printers and Faxes. Right-click blank space in the Printers Control Panel and choose Server Properties (in XP) or Run as Administrator > Server Properties > Continue (in Vista).
Switch to the Driver tab – if your driver is still present, select it and click Remove. If you're using Vista you should leave "Remove driver only" selected only if the drivers were provided by Windows. Click OK followed by Yes > Close.
05. Verify system files
Version: XP, Vista, 7
The System File Checker (SFC) tool enables you to scan for – and replace – corrupt and missing fi les. If you use XP you can use it to scan your entire drive, while in Vista and Windows 7 it can verify individual fi les and folders too. If you have an installation CD, keep it handy in case it's needed.
Step 1. In Windows XP
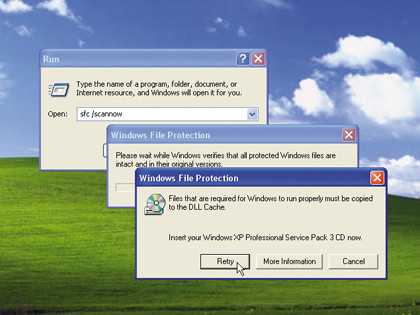
Click Start > Run, type "sfc /scannow" and press [Enter] to check your entire drive for errors. Have your installation CD handy in case you're asked for it.
Step 2. Vista and Windows 7
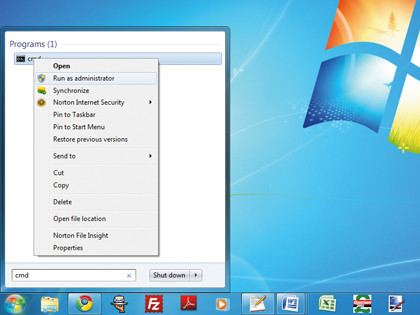
Click Start, type "cmd", then right-click cmd.exe and choose Run as Administrator > Continue. Type "sfc /scannow" and press [Enter] to check your entire drive.
Step 3. Scan and replace
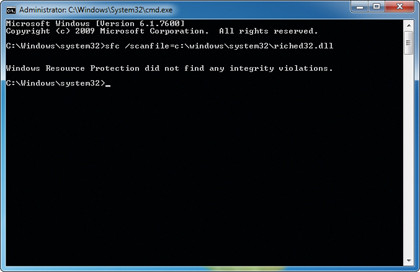
Alternatively, type "sfc /SCANFILE=path \fi lename" and press [Enter], replacing path\fi lename with your chosen fi le – such as c:\windows\system32\riched32.dll.
06. Program compatibility problems
Version: XP, Vista, 7
If you have issues with a program check its website or Google the program's name, version number and your version of Windows to see if there are any issues with it.
Avoid installing system software not listed as compatible with your version of Windows, otherwise try installing it as normal; if it fails, Windows 7 may offer to apply compatibility settings to it – see if these work.
If the program installs but won't run, right-click its program shortcut and choose Properties > Compatibility Settings. Select your old version of Windows from the list and click OK.
If this fails, try ticking "Run this program as an administrator"; in Windows 7 you can also click "Help me choose the settings" to gain access to the Program Compatibility Troubleshooter.
07. PC keeps rebooting after Windows Update
Version: XP, Vista, 7
If your PC gets stuck in a cycle of rebooting during the update process, you need to undo the updates using System Restore. If your computer came without a Windows disc, look for an option to access recovery options, or tap [F8] before Windows starts loading, and then choose "Repair your computer".
If you have an installation disc, boot from it, select your language and then choose "Repair your computer". In both cases, when the menu appears, choose System Restore to undo the update.
08. System Restore not working
Version: XP, Vista, 7
If you're having problems restoring your computer to an earlier state, try booting into Safe Mode (tap [F8] as your PC restarts) and running System Restore from there.
In Vista and Windows 7 there's also another option: you can also run the tool directly from your Windows disc (see tip seven, above) if you can't access Windows.
09. Windows Media Player missing songs
Version: XP, Vista, 7
Tracks missing from Windows Media Player? Try clicking Start > All Programs > Accessories. If you're using XP you should select the Command Prompt, or in Vista or Windows 7 right-click it and choose Run as Administrator.
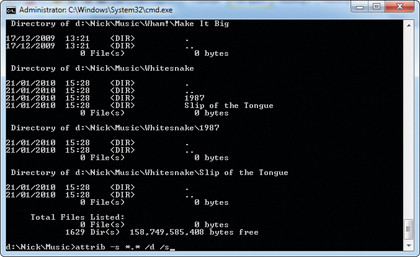
Switch to the folder containing your music using the cd command (for example, cd music cd my documents\my music), then type "attrib -s *.* /d /s" and press [Enter].
Once complete, open Media Player and press [F3], or choose Tools > Advanced > Restore Media Library (in Windows 7) to access all your music again.
10. Action Center
Version: 7
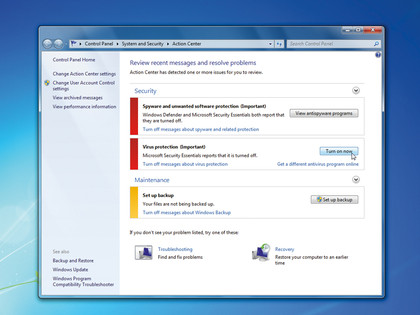
Click the flag icon in the Taskbar's notification area to access the Action Center. Here you can get an at-a-glance look at problems, plus launch a series of troubleshooters to help quickly fix the problems that plague you, without getting your hands dirty.
11. Show printer ink levels
Version: XP, Vista, 7
If you've just upgraded to a new version of Windows and can't access your printer's ink levels, the bad news is that Windows installed a basic driver without the function.
Check the manufacturer's site for a dedicated driver and – if it exists – install that.
12. Fix Windows driver problems
Version: XP, Vista, 7
Most hardware problems can be traced to the drivers, the software that enables them to work with Windows. When it comes to tracking down problems, the first port of call should be Windows' own Device Manager – here's how to troubleshoot problems using this useful tool.
Step 1. Open Device Manager
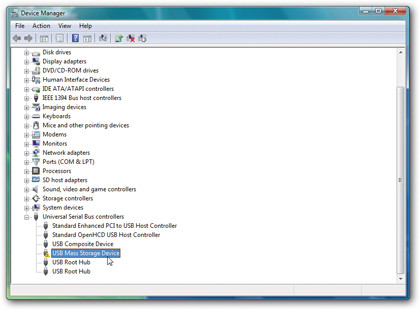
Press [Windows] + [R], type "devmgmt. msc" and press [Enter]. Look for yellow exclamation marks next to troublesome hardware devices and double-click one.
Step 2. Get error details
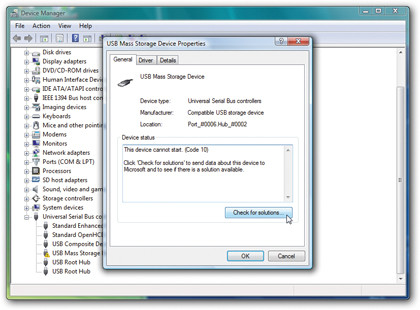
Look on the General tab for an error code and description of the problem – if a troubleshoot button is present, click it to see if you can fi x the problem easily.
Step 3. Search online
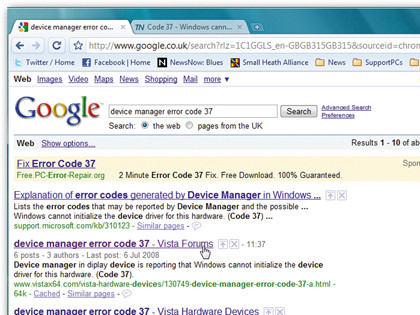
If no fix is forthcoming, use the error details as part of your web search – try a general search first, then add your hardware's make and model if necessary.
13. Resolve ReadyBoost conflict
Version: Vista, 7
Your PC can only use one ReadyBoost device at a time, and some computers come with built-in flash memory already configured for use with ReadyBoost.
To resolve this conflict click Start, rightclick Computer and select Manage, then under Storage choose "Disk Management" to verify the existence of such a drive. Look for a program called Intel Turbo Memory Console (type "Intel" into the Start menu's Search box) and open this to disable the built-in drive in favour of your own.
14. Folder settings not remembered
Version: XP, Vista, 7
If you find you can no longer customise folders to look and behave how you want, the solution involves some editing of with two Registry subkeys – BagMRU and Bags – which are found in two separate locations: Shell and ShellNoRoam under HKEY_ CURRENT_USER\Software\ Microsoft\Windows.
Think this sounds like too much hassle? No problem, just open the Microsoft Fix It Center tool (see tip three) and run the "Diagnose and repair Windows Files and Folder Problems" wizard. This will do the hard work for you.
15. PC keeps rebooting
Version: XP, Vista, 7
If your PC restarts unexpectedly after briefly displaying a blue screen, then it's encountered a STOP error. If this keeps occurring you need to identify it.
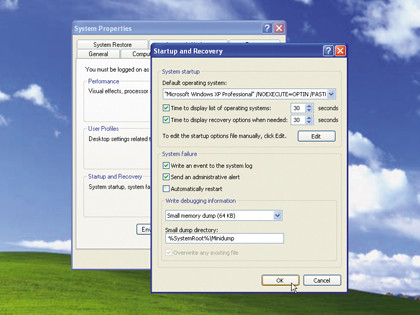
In Vista and Windows 7 you can stop Windows automatically restarting from the Windows boot menu that should appear; if you use XP click Start, right-click My Computer and select Properties > Advanced tab. Click Settings under "Startup and Recovery" and untick "Automatically restart" before clicking OK twice.
Now when the STOP error occurs you'll see a blue screen with details of the error message; note down the description, any files it refers to, and the STOP error code. Then search the web for these terms to hopefully find a solution.
16. Blocked startup programs
Version: XP, Vista, 7
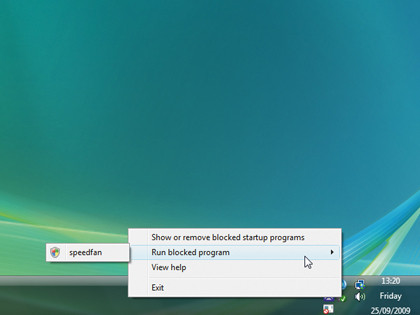
If you get this message after starting Windows, it means one of the programs set to start with it is attempting to work with elevated privileges. This is symptomatic of older programs, so either source an update or an alternative program if you can.
Right-click the message, choose "Run blocked program" and select the errant tool in question. Then click Continue when prompted.
17. Fix file-sharing problems
Version: XP, Vista, 7
Verify your PCs are on the same network – wireless or wired – and all on the same workgroup (click Start, right-click Computer and select Properties; in XP you need the Computer Name tab). Is File and Printer Sharing enabled?
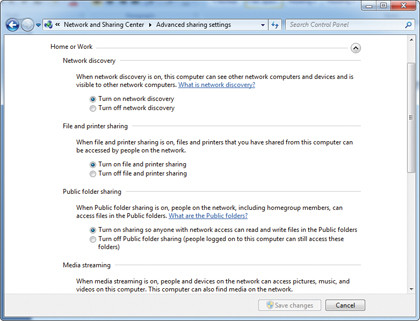
Check from the Network and Sharing Center in Vista/Windows 7 – ensure your network is Home or Work. In Windows 7 click Choose homegroup and sharing options > Change advanced sharing settings; in XP right-click a folder and choose Properties > Sharing tab.
Disable password protected filesharing in Vista or Windows 7 if sharing with PCs running XP, and check your firewall has placed your network in a trusted zone.
18. Access denied error on system files
Version: XP
Not long ago dealing with "access denied" errors relating to system files or the Registry involved downloading a tool and typing out a complex script.
Now you can resolve this issue – sometimes found when installing SP3 – by downloading a dedicated fix-it tool from http://go.microsoft.com/?linkid=9730795.
19. Low memory error
Version: XP, Vista, 7
Fix this problem by making sure Windows is set to handle your virtual memory settings; open the System Control Panel and either click "Advanced system settings" or switch to the Advanced tab.
Then under Performance click Settings, select Advanced and click Change. You need to verify that either "Automatically manage paging file for all drives" (in Vista or Windows 7) or "System managed size" (in Windows XP) is selected, then if necessary click Set > OK, rebooting when prompted.
20. No sound in Windows
Version: XP, Vista, 7
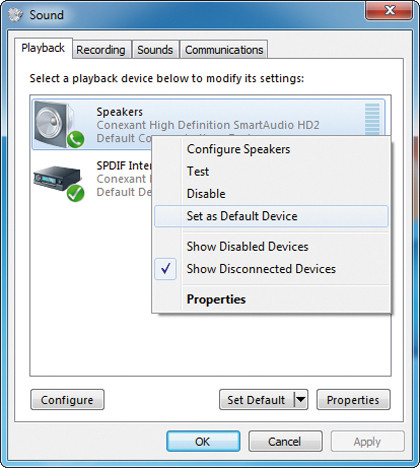
Before running the Microsoft Fix It Center tool (see tip three), open the "Sound" or "Sounds and Audio Devices" Control Panel.
Select the Playback or Audio tab, and verify the device is set to be the default; if not, select it from the list to fix the problem.
21. Create a repair disc
Version: 7
If your PC didn't come with a Windows installation disc, click Start, type "backup" and click Backup and Restore.
Select "Create a system repair disc" and put a blank CD or DVD in your writeable drive to create a bootable disc with the "Repair your computer" options on it.
22. Where's GPEDIT?
Version: XP, Vista
If you're running one of the Home editions of Windows, you'll find the gpedit.msc tool is missing. If you're instructed to fix a problem using this tool and you're running Windows XP, visit here to find the equivalent setting in the Registry.
Alternatively, for the Home edition of Vista you can download an Excel spreadsheet with the various settings from here.
23. System Restore problems
Version: XP, Vista, 7
Restore points are cumulative in reverse – each new one only saves what's changed – so old points rely on newer ones to work; if one corrupts then all older ones are lost. That means the older a Restore point, the less reliable it is, so avoid using anything but the most recent one.
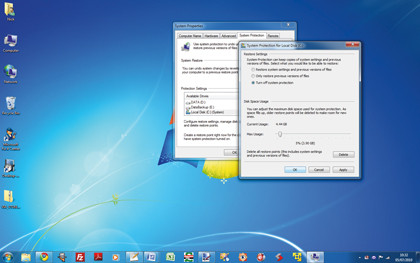
Open Disk Cleanup (Start > All Programs > Accessories > System tools) and – if prompted – choose "all users". On the More Options tab delete all but the newest Restore point. If all else fails, disable System Restore and lose all Restore points, then re-enable it.
For XP use the tool here; in Vista and Windows 7 open System Protection, untick all the boxes and click Turn off System Restore > Apply. Tick your system drive again and click Apply to switch it back on.
If you're plagued with specific error messages, or System Restore doesn't work well, you'll find useful solutions here.
24. Text too small
Version: XP, Vista, 7
If you're struggling to read the text on your screen simply right-click the desktop and choose "Personalization" or "Properties". In Windows 7 click Display, or in Vista select "Adjust font size (DPI)"; in XP switch to the Settings tab and click Advanced.
Select a larger size to suit you and click OK twice followed by Yes > Close, rebooting if prompted. Certain programs will throw up warnings – in Vista and Windows 7 you can right-click the program shortcut and choose Properties > Compatibility tab, then tick "Disable display scaling on high DPI settings".
25. Video display problems
Version: XP, Vista, 7
When playing back video on your PC, does the screen appear too light or dark, or is the colour balance all wrong? That's because the video uses special "overlay" settings in place of Windows' own.
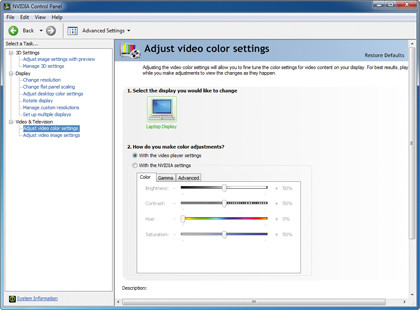
To resolve this, right-click the desktop and look for an Nvidia or ATI option; if it's not there, choose "Personalization" or "Properties" instead. Choose Settings or Display Settings and look on the tabs for a video or advanced option.
Once located, make sure the video settings are set to that of the player, and not your graphics adaptor. When this is done, save your settings to resolve the problem.
26. Use Event Viewer
Version: Vista, 7
Windows records all major events, including errors and warnings, which can be accessed for troubleshooting. Press the Windows key and [R], type "eventvwr.msc" and press [Enter]. Now expand Windows Logs and click on a log.
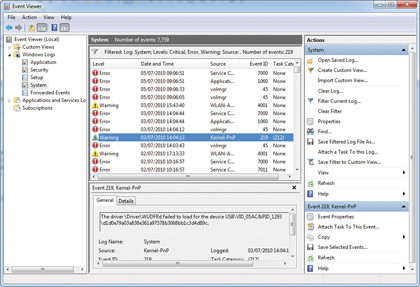
Click Filter Current Log, tick Critical, Error and Warning and click OK. Click an event that occurred around the time of your problem: each event will provide more information about your problem – if there's a link to more help online, select it.
Some events won't produce any extra information, but many will; you may even get possible solutions to try, but if not, make a note of any extra detail to use in a Google search.