Why you shouldn't write off Windows 10 Mobile just yet
Microsoft could still do the business with smartphones…
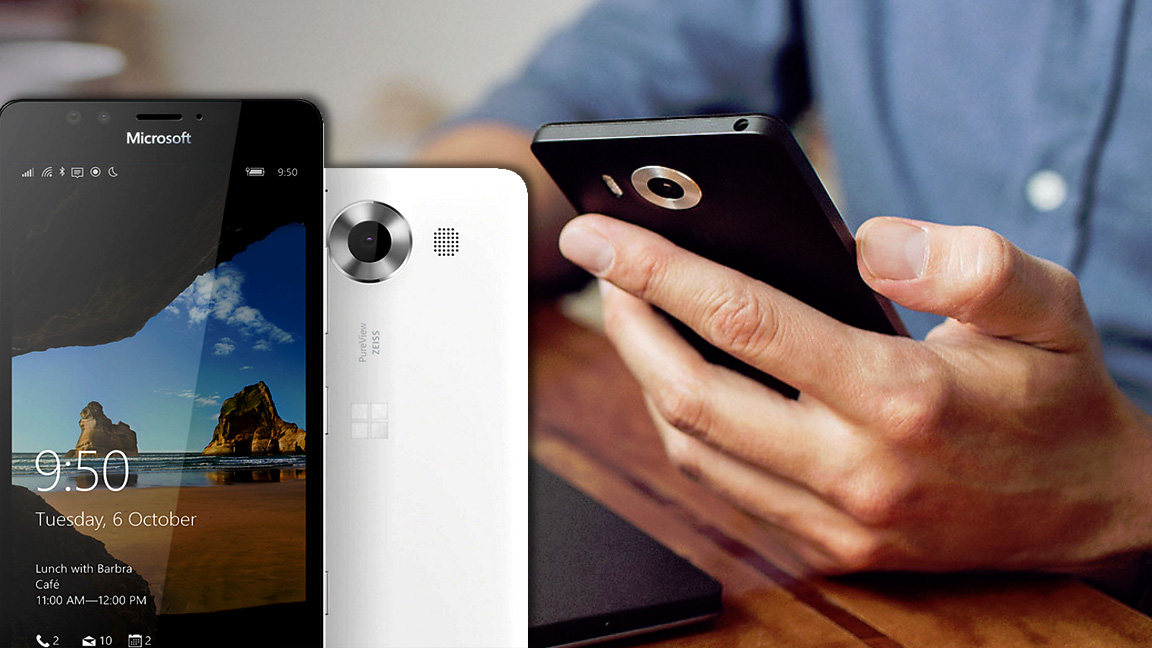

Microsoft has never had much success with its mobile phone business, and buying Nokia for $7.2 billion (around £5.5 billion, AU$9.7 billion) back in 2013 didn't help Redmond claw its way to relevancy, either.
Revenues from its phone business, which includes Lumia-branded handsets, dropped over 70% in the three months leading up to July, on top of a 50% decline in the quarter before that, and a similar drop in the previous quarter.
Research firms, such as Gartner and IDC, peg the market share of Windows 10 Mobile at somewhere between zero and 1%, a figure that could also be described as a rounding error equivalent to BlackBerry's share of the market.
Billion blunder
The company hasn't been releasing many new handsets of late and recently revised its stated goal of getting Windows 10 onto one billion devices by 2018 because of "the focusing of our phone hardware business."
The "focusing" in question is, by and large, a mystery. Microsoft declined to show off any new Windows 10 Mobile details earlier this year at its Build conference, and after this was picked up on by the media, Redmond was subsequently forced to release a statement clarifying its commitment.
The platform the company built with Windows 10 has been growing and now has 350 million active users across a range of devices, including Xbox, PCs, tablets, and (some) smartphones. But the downward revision of the big billion goal – and its reasoning – is embarrassing for Microsoft and signals just how far its mobile ambitions have fallen.
There is, however, a way to turn this around.
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!
Deep and meaningful relationships
Microsoft has always had the best, by which we mean the deepest, relationships with big enterprise customers who run Windows, use Office, and most likely have some kind of Azure setup humming in the background.
While Amazon has snapped up growing startups with its Amazon Web Services platform, Microsoft has retained many big clients, which are defined as companies with over 100,000 employees, $10 billion (around £7.5 billion, AU$13.5 billion) in revenue per year, or both.
According to Gartner, Microsoft software and services are used in these kinds of companies the majority of the time, and the dominance only starts to fade as the organisations become smaller than 250 employees or generate less than $50 million (around £38 million, AU$67 million) in revenue.
As you'd expect, the bigger the company the more money Microsoft generates from it. Office 365, the cloud version of its productivity software, is used by over 23 million people, many of which are employees of big firms.
These relationships – which are likely years old – could be used to sell Windows-based smartphones.

Advantage Microsoft
"In the enterprise segment, Microsoft has a chance," said Francisco Jeronimo, a senior researcher at IDC, in an interview earlier this year. "They are looking at selling a bundle of products and services, rather than just the operating system, and when they go to a client and offer a device that comes with Continuum, the docking station, and Windows 10, it can be quite interesting."
The features that Microsoft has developed for its mobile operating system are some of the best-in-class. Continuum, for example, uses a $99 (around £75, AU$133) dock – called the Display Dock – which attaches to a mouse and keyboard to turn a Lumia smartphone into a fully-fledged computer running Windows 10.
Demos of a smartphone turning – literally – into a computer are really impressive and, more importantly, represent something only Microsoft is doing currently. Apple, which makes the iPhone, chooses to keep its desktop and smartphone operating systems separate, and Google, which develops Android, has chosen never to merge Chrome OS and Android in any meaningful way.
So, either by design or by accident, Microsoft has a huge, marketable advantage that would be uniquely beneficial to enterprise customers.
Max Slater-Robins has been writing about technology for nearly a decade at various outlets, covering the rise of the technology giants, trends in enterprise and SaaS companies, and much more besides. Originally from Suffolk, he currently lives in London and likes a good night out and walks in the countryside.