DDR5 vs DDR4 RAM: what's the difference?
We look at the most recent iteration of memory technology, present in laptops, desktops and even smartphones.
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
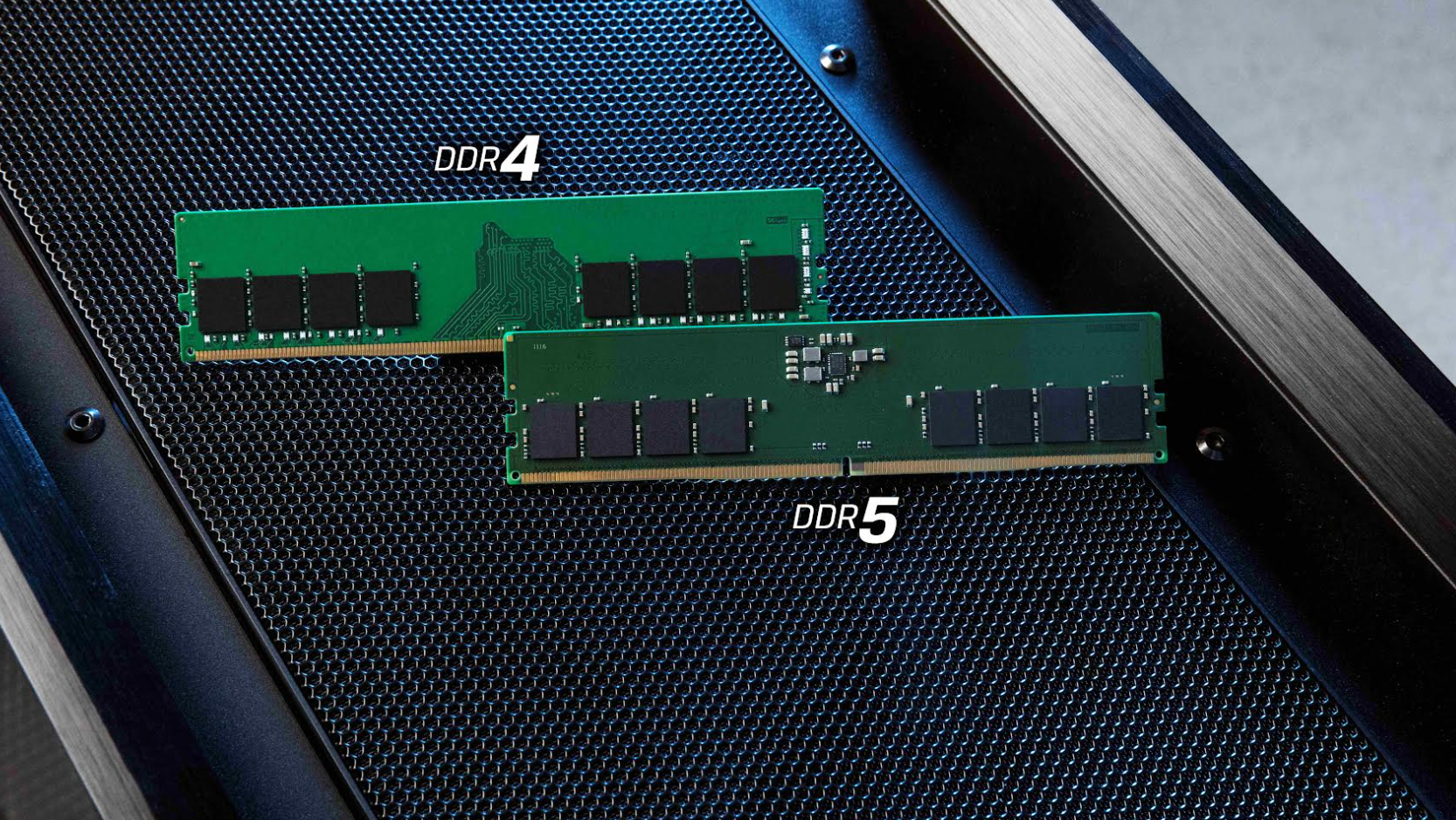
DDR5 is the fifth generation of Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (RAM). That’s quite a mouthful, hence its useful acronym - DDR5. When it was debuted in 2021 it came with a clutch of great features that were designed to deliver considerable enhancements in performance and capacity, to consume less power and deliver greater efficiency.
Tl;dr, DDR5 memory is designed to provide enhanced scalability, making it easier for companies to expand their tech stacks and upgrade systems in the future. Its higher data rates, increased capacity, and improved power efficiency offer a future-proof solution for businesses looking for an improved total cost of ownership and to maximize the lifespan of their hardware investments.
But how does it compare with DDR4, its predecessor? And why should enterprises consider upgrading their RAM now rather than replacing entire systems? That’s what this article will look at.
1. Speed
One of the most significant differences between DDR4 and DDR5 is the data transfer rates. DDR4 memory operates at speeds ranging from 2133 MT/s up to 3200 MT/s. On the other hand, DDR5 starts at a base speed of 4800 MT/s and is expected to reach up to 6400 MT/s in line with compute platform releases. The higher data rates offered by DDR5 represents a 50% increase in bandwidth, which for users means faster processing and smoother multitasking.
2. Capacity
DDR5 brings a substantial increase in module capacity compared to DDR4. DDR4 modules have a maximum capacity of 32GB, while DDR5 modules start at 16GB and are anticipated to reach capacities of up to 128GB. The increased capacity will allow enterprises to run more demanding applications and games and extend the capabilities of existing systems. (ed: they also offer exotic capacities as well, e.g. 24GB)
3. Power Efficiency
DDR5 memory operates at a lower voltage – sub-1.1V compared to DDR4's 1.2V, resulting in improved power efficiency of up to 20%. Not only does this help to conserve battery life in laptops and assist enterprise servers that are operating 24/7, it also contributes to reduced overall power consumption, lower heat generation, and extended component lifespan. DDR5 also has a new command, SAME-BANK Refresh, which allows a refresh of just one bank per bank group, versus all banks. All together these new features boost performance and efficiency and have the potential to cut costs for businesses.
4. Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMIC)
DDR5 modules have on-board PMIC and this regulates the power needed by components of the memory module such as DRAM, register and SPD hub). For server-class modules the PMIC users 12V and for PC-Class modules, it uses 5V. This means improved power distribution over the DDR4, better signal integrity and less noise.
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!
5. On-Die ECC Support
DDR5 memory, unlike DDR4, incorporates built-in Error Correction Code (ECC) support, a new feature which can correct bit errors within the DRAM chip. On-die ECC enhances data integrity, increases reliability and reduces the risk of data corruption. This feature is particularly useful in professional and high-performance computing environments where data integrity is crucial. Think servers, workstation PC etc.
6. Bandwidth and latency
DDR5 memory is split into two independent 32-bit addressable subchannels, effectively offering doubled memory banks. This lowers the latencies of data access for the memory controller resulting in improved overall bandwidth. While the data width of the DDR5 module is 64-bit, like the DDR4, splitting it into two channels increases overall performance. For enterprises, this means faster data transfers compared with DDR4, and applications that require low-latency performance, such as gaming or real-time data processing systems, are better supported without any compromise in performance. In addition, DDR5 uses Decision Feedback Equalization (DFE) to provide stable, reliable signal integrity, which also enables high bandwidth.
7. Compatibility
DDR5 and DDR4 memory modules appear similar however significant changes in their form factors means that DDR5 modules are not compatible with legacy systems. This is due to differences in architecture and pin configurations; because of this it is important that businesses check that the RAM module they are purchasing is supported by their motherboards.
Remember that DDR5 is also present in SODIMM formats (for laptops) and as LPDDR5 for smartphones and other ultra thin designs.
In summary, In the current technological landscape, businesses face increasing demands for faster and more efficient systems but are highly conscious of the costs attached to ripping out and replacing. Upgrading to DDR5 memory has a significant part to play in the adoption of an ‘upgrade rather than replace’ strategy, providing a cost-efficient approach to boosting performance and maximizing the value of their existing systems. In terms of productivity, disruption to workflows and minimizing downtime, upgrading RAM is considerably more straightforward than replacing systems.
In conclusion, the key differences between DDR4 and DDR5 memory technologies demonstrate the advantages of adopting DDR5 for businesses looking to enhance system performance and longevity. By upgrading RAM rather than replacing entire computers and assets, businesses can save costs, optimize resource utilization, and keep pace with the ever-evolving demands of the digital world.
Regional Director for UK & Ireland and DRAM Business Manager for the EMEA Region at Kingston Technology.
