TechRadar Verdict
Hyper-V is one of the best virtualization software for Windows-powered PCs or servers.
Pros
- +
High performance
- +
Scalability
- +
Redundancy
- +
Very secure
Cons
- -
Windows-only
- -
Costly management console
- -
Consumes CPU/memory
Why you can trust TechRadar
Microsoft released the first version of Hyper-V in 2008 under a different name, Windows Server Virtualization. The first version was compatible only with Windows Server 2008, but it has since been released on many successive versions of the Windows Server. You can also use it on select versions of Windows operating systems for laptops and desktops.
Hyper-V is a hypervisor that lets users create virtual machines on Windows-based x86-64 systems. There are separate versions for the typical operating systems (Windows 8, 10, etc.), Hyper-V, and the Windows Server OS, Hyper-V Server.
Unfortunately, Microsoft stopped releasing new versions of Hyper-V Server in 2019, encouraging users to switch to the Azure Stack HCI to host virtualized workloads. But, it’s contractually bound to support the last release until 2029.
Microsoft Hyper-V: Plans and pricing
Hyper-V is free to download, and you can use it without limit on the CPUs, RAM, or primary storage. However, the management layer comes at an extra charge. This layer, the Microsoft System Center, enables you to operate Hyper-V from a graphical user interface. It doesn’t come cheap, with license costs starting from $1,323 per year.
It’s not mandatory to pay for System Center, just more convenient. If you don’t get the license, you can use Hyper-V for free but operate it only through a command-line interface.
Microsoft Hyper-V: Features
Hyper-V is a hypervisor that lets you create and run virtual machines (VMs). A virtual machine is a software that emulates the functionality of a separate computer. Having multiple VMs is like having various computers drawing their resources from a single hardware system.
There are many use cases for virtual machines. For example, if you want to run a software that's no longer available for the current version of your operating system, you can install the older OS on a virtual machine and run it. You can also use a virtual machine to simulate how malware can affect a PC.
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!
There are two types of hypervisors; Type-1, which has direct access to the hardware, and Type-2, which relies on a host operating system. As a type-1 hypervisor, Hyper-V offers sharp performance because it has direct access to the hardware to execute functions instead of going through an additional OS layer. It also avoids the security vulnerabilities that come with an OS.
Hyper-V lets you create virtual machines running many operating systems, including different releases of Windows, Linux, and FreeBSD.
There's a separate Hyper-V for Windows and Hyper-V for Windows Server. The former is available on 64-bit versions of Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, and Education– it isn’t compatible with the Home edition. Windows Server is a separate operating system for managing servers, not desktops or laptops.
The core difference between Hyper-V on Windows and Hyper-V on Windows Server lies in their memory management model. On a server, Hyper-V memory works with the assumption that only the virtual machines are running on the server. Hyper-V on Windows manages memory with the assumption that most client machines are running other host software in addition to virtual machines.
Generally, Hyper-V lets you run one or more virtual machines on a computer with 4GB of RAM. But, you'd need much more than 4GB of RAM if you want to run intense software like games and video editing tools on your virtual machines.
Notable components of Hyper-V include;
A virtual machine you install using Hyper-V uses the same parts as a physical computer, including processor, storage, memory, and networking. The difference is that multiple virtual machines will draw all these capacities from a single hardware.
You can configure the memory, processor, storage, and networking features like with a typical computer.
Each guest operating system that Hyper-V lets you create has a customized set of services and drivers, called integration services, that make it more convenient to use the OS in a virtual machine.
Examples of such integration services include the Heartbeat Service, which reports if a virtual machine is running correctly or not; Time Synchronization Service, which synchronizes a virtual machine's clock with the host system's clock; and the Data Exchange Service, which enables the virtual machine and its host to exchange metadata.
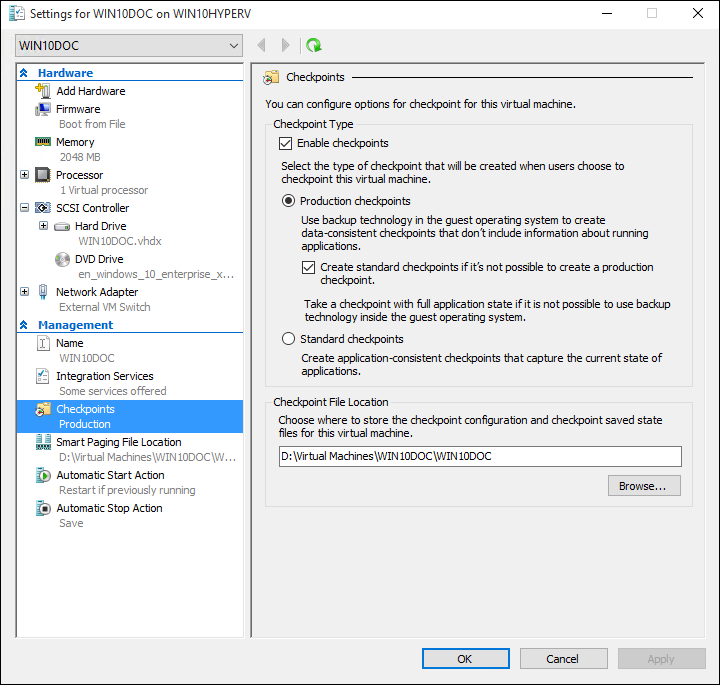
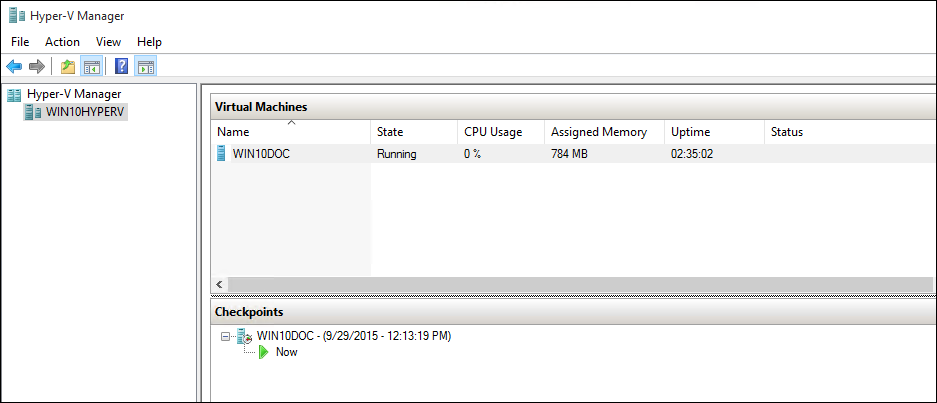
Hyper-V has a feature that creates copies of virtual machines that you can store in another location. Hence, if your virtual machine gets corrupted, you can always restore it from the copy.
You can migrate virtual machines from one device to another with ease. Hyper-V supports Live Migration, which lets you move running virtual machines from one Hyper-V host to another without experiencing downtime. You can also migrate a virtual machine's storage from one location to another without any compatibility challenges.
You can connect to a Hyper-V virtual machine from another host and use it without hitches. Hyper-V gives console access, meaning you can see what's happening in a virtual machine even if its operating system hasn't been booted.
Microsoft Hyper-V: Interface and use
If you’re using the free version of Hyper-V, you’ll have to operate it via a command-line interface, which involves using codes to execute functions. You’d need to memorize the codes, which can be challenging for a non-technical user. To make things easier, you can pay for Microsoft System Center, which gives you a graphical management console, but the price is steep.
Microsoft Hyper-V: Support
Microsoft provides customer support through email, live chat, and telephone. Its website also has comprehensive documentation concerning all Hyper-V functionalities, which is a good resource for learning about the software and how to solve any challenges you may encounter.
Microsoft Hyper-V: The competition
ESXi, a VMware product, is the best alternative to Hyper-V that we’d recommend. It’s reliable, scalable, and provides more options to configure your virtual machine compared to Hyper-V.
Microsoft Hyper-V: Final verdict
Windows OS users are already used to Microsoft products, so Hyper-V is an ideal choice for them. It allows users to take advantage of Windows OS features better than most other virtualization software. The main drawback is having to pay a considerable sum for a management console.
We've featured the best remote desktop software.
Stefan has always been a lover of tech. He graduated with an MSc in geological engineering but soon discovered he had a knack for writing instead. So he decided to combine his newfound and life-long passions to become a technology writer. As a freelance content writer, Stefan can break down complex technological topics, making them easily digestible for the lay audience.