Sponsored by

Business process automation: The ultimate guide to saving time and money
AI for one, can help businesses automate processes faster

Automation has always been a key focus for businesses, and the recent artificial intelligence (AI) boom has further entrenched it.
Many businesses seek ways to automate redundant processes and reduce overhead costs, but this requires careful deliberation. The wrong automation strategy can cause even more problems and cost more than the previously manual method.
I’ve created this guide so that you don’t make mistakes with your automation processes. Read on to learn practical tips for effective automation and why automation is important in all business niches.
Exclusive offer: Get real-time data from any website with Web Scraping API
Start your 7-day free trial with 1K requests and scrape data with a click. Unlock 100+ ready-made scraping templates, 100% success rate, advanced geo-targeting, and automated IP rotation. Don’t miss out – collect data without CAPTCHAs or geo-restrictions.
TechRadar Pro Approved Sponsored Offer
What is business automation?
Automation simply means using technology to perform repetitive tasks, with minimal or no human input. It can be a basic task like recording sales in a balance sheet, or a complex task like building an AI chatbot to resolve routine issues for customers.
Here’s an example you encounter frequently– you walk into a store, pick your items, and head to the cashier’s table. The cashier scans each item with a barcode scanner, and the price immediately pops up on the screen.
That’s a key automation that saves retailers huge time– otherwise, cashiers would have to manually check for each item’s price, and the queues would be unbearable.
In the above example, the automation doesn’t end after an item gets scanned. After all items are tallied and you pay, the transaction will be automatically recorded in the retailer’s bookkeeping system.
Automatic recording ensures accurate results, as humans are prone to error when dealing with complex figures. The retailer is assured of precise sales figures. A lot more processes are automated in a retail outlet, but the cashier’s section is the most common one you’ll encounter.
There are endless other examples of how automation underlines the modern economy. Without it, we won’t enjoy close to a fraction of the abundance of goods and services we do. Man plus machine delivers sky-high productivity for businesses, and any firm that ignores automation is at a key competitive disadvantage.
What processes are often automated?
Businesses focus on automating repetitive and redundant processes. In our earlier example, imagine the cashier had to repeatedly type the details of each product into their PC– that’ll be hectic, so automation becomes necessary.
Here are some common tasks that businesses automate:
Bookkeeping
With the right accounting software, you can automate routine bookkeeping processes for your business. Every transaction will be automatically recorded and classified according to your parameters. The same applies to every expense, although you may need a separate expense management platform for this.
At the end of each day, week, month, quarter, or year, you’ll simply review the financial records and provide final approval. Automated bookkeeping saves small businesses a lot of money they would have spent on in-house accountants.
Customer service
At some point, you’ve likely gotten tired of replying to the same routine requests from different customers. People want to find out the price of a product, your shipping times, accepted payment methods, and working hours, and you’ll keep typing similar replies to them. It gets tiring and leaves less time to address complex customer complaints.
You can create chatbots that automatically reply to mundane inquiries, then direct customers to support staff for complex issues. You’ll be surprised by how much more productive your support team becomes.
The recent rise of AI models has been a boon for small businesses. You don’t need advanced programming skills or to enlist a developer to build a chatbot. Many platforms now let you create and deploy chatbots through a drag-and-drop interface.
The chatbots aren’t just replying according to a script; they use AI to analyze a customer’s inquiry and respond properly. If the inquiry is beyond the chatbot’s abilities, the issue gets escalated to a support team member.
Email marketing
You’re a business owner, but let’s switch to a customer’s perspective for a moment. You’ve likely ordered an item from a store and received an immediate email confirmation.
Then, you also received an email alert after your product was delivered, and probably a follow-up email asking about your experience with it. No human was typing these emails by hand– they were all automated email marketing campaigns.
Now, back to a business owner’s perspective, you can automate email marketing campaigns to keep customers engaged. Along with email alerts when a customer orders an item, you can send regular emails promoting new products they may be interested in, or time-limited discounts they can grab immediately. People won’t hesitate to grab a good deal sent directly to their email address.
To make email campaigns more effective, you can personalize them with “Hi, [Customer’s Name]” or “Dear [Customer’s Name].” Personalization makes the email feel unique to the customer, and they become more willing to follow your suggestion.
Key steps for effective business process automation
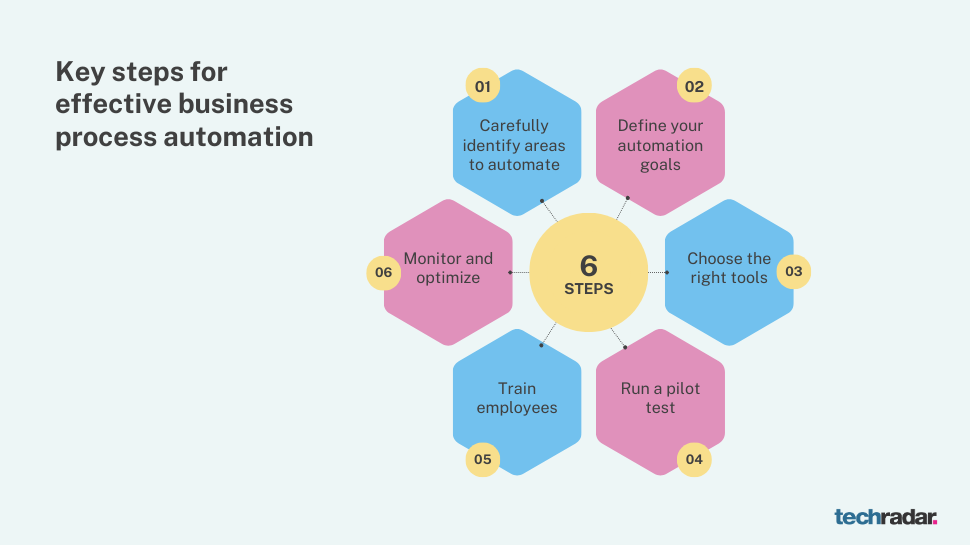
1. Carefully identify areas to automate
It starts with carefully analyzing your operations to decide which areas to automate. This process is rigorous and, ironically, can’t be automated. Examine your operations and list the repetitive, time-consuming tasks you need to automate.
For example, you may observe your accounting team spending too much time on filing and sorting expenses. This task can be automated with an expense management tool that automatically records every transaction from a corporate card, and employees can scan the receipt for future reference.
Every expense will be automatically classified based on its receipt details. With this automation, your accounting team doesn’t become redundant– instead, they’ll have more time for other tasks, like preparing tax records.
2. Define your automation goals
After identifying key areas to automate, define what you want to achieve with the automation.
In the above example, the goal could be to reduce expense processing time by 75%, or to lessen your spend on hiring external accountants.
You can use the SMART framework (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) as a goal-setting guide. This step is a simple, practical one based on your business needs.
3. Choose the right tools
The next step is selecting the right tools to automate the identified tasks. This selection should be carefully considered, as the wrong tool can introduce even more friction for your business.
For example, a business seeking to automate expense recording needs a proper expense management platform fitting its budget, headcount, and spending range.
Businesses can find affordable expense management tools with basic features or costlier options with advanced features like OCR receipt scanning and real-time spending controls.
Conduct extensive research before choosing a tool. TechRadar’s guides are a good starting point, providing in-depth information about every popular software tool you can think of.
You can check our buying guides on the best expense tracking apps, retail point-of-sale systems, invoicing software, and many more tools that help automate your business operations.
4. Run a pilot test
Run a small pilot test for any tool your business wants to adopt. This test program helps you and your staff get familiarized with the tool and point out any flaws.
Many platforms offer 14 to 30-day free trial periods so that you don’t have to pay before this pilot test.
For example, if you’re deploying an expense management platform, run a 30-day trial where employees spend money with corporate cards, and the accounting team receives automated reports.
Seek feedback from all involved parties– employees should be comfortable with interacting with the expense management app, and accountants should certify that the app lets them track expenses effectively. They should note any flaws that need to be corrected or worked around.
During the pilot stage, the identified flaws may be too many, and you’ll have no choice but to discard the tool and find an alternative.
It may be stressful, but you’re better off testing repeatedly to choose the best tool. Automation tools are designed to increase productivity, but selecting the wrong one can have the opposite effect.
5. Train employees
If the pilot stage is satisfactory, you can begin rolling out the platform for all relevant employees. You should provide training resources to help employees get used to the tool, from written user guides to tutorial videos, FAQs, and live training sessions.
If your company has an in-house IT team, they can organize interactive learning sessions for employees. Training might seem hectic, but it’s a worthwhile investment that prevents employees from making serious mistakes.
6. Monitor and optimize
Your tool has finally been deployed, but that's not the end. More things may need to be automated in the future, and existing processes may need to be tweaked.
You should continually analyze your business processes to identify any areas that need adjustment. That’s what guarantees saving time and money in the long term.
Monitor how competitors automate their processes and stay up to date on industry trends. Automation is a race, and any company that gets complacent risks getting left behind.
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!
Stefan has always been a lover of tech. He graduated with an MSc in geological engineering but soon discovered he had a knack for writing instead. So he decided to combine his newfound and life-long passions to become a technology writer. As a freelance content writer, Stefan can break down complex technological topics, making them easily digestible for the lay audience.